How to Deploy an Application on a Kubernetes Cluster
How to Deploy an Application on a Kubernetes Cluster
This document provides step-by-step instructions for deploying an application on a Kubernetes cluster.
Step 1: Prerequisites
Ensure the following are set up before proceeding:
Kubernetes cluster is up and running.
kubectl is configured to interact with your cluster.
Docker image of your application is available in a container registry (e.g., Docker Hub).
Proper access to the cluster and namespace (if using role-based access control).
First of all deploy a kubernetes cluster download its config file and
export it on your local server with command:-
export KUBECONFIG=test.yml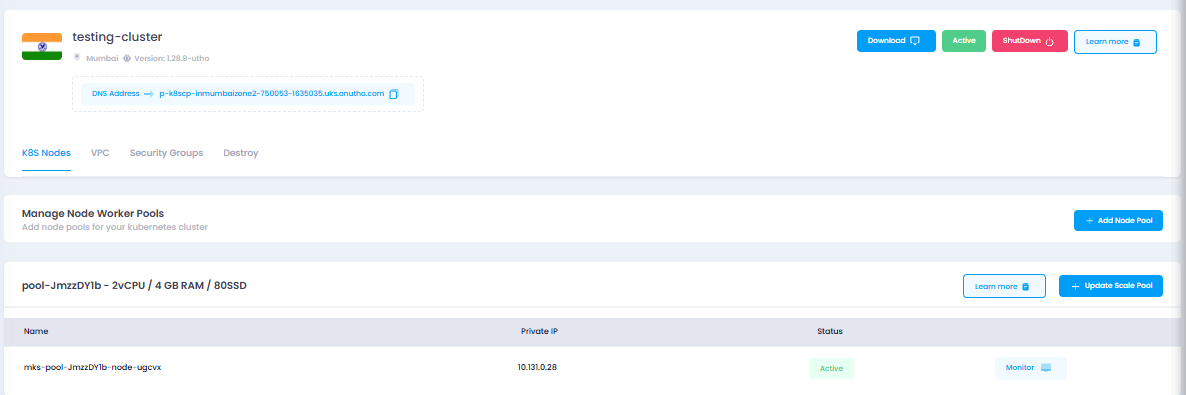
After that install the kubectl packages with command:-
snap install kubectl --classicKubectl get nodesYou will see your connected nodes on server
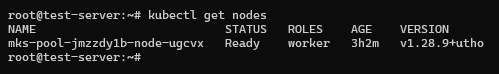
Step 2: Create a Deployment YAML
Create a YAML file for your application’s Deployment. Below is an
example for an application using the nginx image:
Save this file as deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80Step 3: Create a Service YAML
To expose your application, create a Service YAML file. For a
LoadBalancer:
Save this file as service.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancerStep 4: Deploy Resources to Kubernetes
Apply the Deployment YAML:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yamlApply the Service YAML:
kubectl apply -f service.yamlStep 5: Verify the Deployment
Check the status of your Deployment:
kubectl get deploymentsExample output:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE\
nginx-deployment 2/2 2 2 5m
Check the status of the Service:
kubectl get servicesExample output:
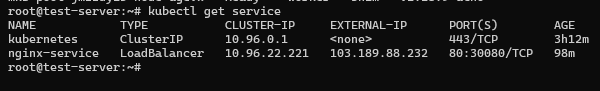
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE\
nginx-service LoadBalancer 10.96.22.221 103.189.88.232 80:30080/TCP 5m
Step 6: Access the Application
If you created a LoadBalancer Service, find the EXTERNAL-IP from the
Service output.
Open your browser or use curl to access the application:
http://EXTERNAL-IP:80
Example output:
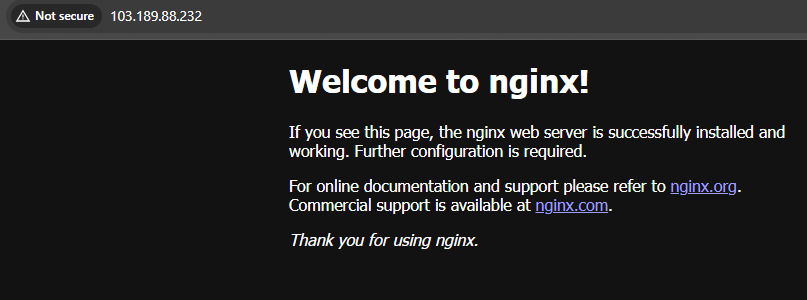
If successful, you should see the application’s welcome page (e.g.,
Nginx default page).
Step 7: Troubleshooting
Check pod status if something isn't working:
kubectl get podsExample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE\
nginx-deployment-7c79c4bf97-w8md8 1/1 Running 0 5m
Describe the pod for detailed logs:
kubectl describe pod POD-NAMEReview logs of the pod:
kubectl logs <POD-NAME>Check the Events section in your Service or Deployment description:
kubectl describe svc nginx-servicekubectl describe deployment nginx-deploymentStep 8: Cleanup (Optional)
If you want to remove the deployment and service:
Delete the Deployment:
kubectl delete -f deployment.yamlDelete the Service:
kubectl delete -f service.yamlThank You!