How to add a swap file in Linux

Introduction
In this article, you will learn how to add a swap file in linux.
A swap file is a system file that creates temporary storage space on a solid-state drive or hard disk when the system runs low on memory. The file swaps a section of RAM storage from an idle program and frees up memory for other programs.
The term “swap space” can refer to either a partition on the disc or a file. During the installation process, users have the ability to create a swap space, or at any other point in the future if they so want. There are two applications for swap space: the first is to extend the virtual memory beyond the amount of installed physical memory (RAM), and the second is to provide support for suspending to disc.
Step 1 – Login as the Root User
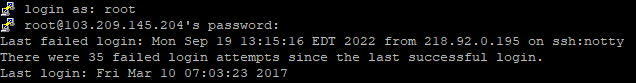
Step 2 – Create Storage File
To make a 512MB swap file (1024 * 512MB = 524288 block size), run the following command:
#dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile1 bs=1024 count=524288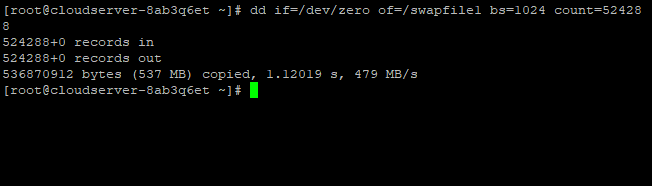
Step 3 – Secure swap file
For security reasons, enter the following file permissions:
#chown root:root /swapfile1#chmod 0600 /swapfile1A globally accessible swap file is a major local vulnerability. The commands above ensure that only the root user can read and write to the file.
Step 4 – Set up a Linux swap area
To create a swap file in Linux, enter the following command:
#mkswap /swapfile1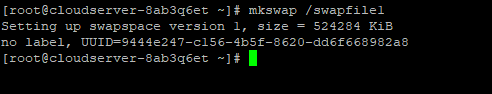
Step 5 – Enabling the swap file
Finally, immediately activate the /swapfile1 swap space by typing:
#swapon /swapfile1Step 6 – Update /etc/fstab file
Adding a line to the /etc/fstab file will make /swapfile1 accessible following a reboot of the Linux system. To read this file, launch a text editor like vi.
#vi /etc/fstabPlease add the following clause:
/swapfile1 none swap sw 0 0
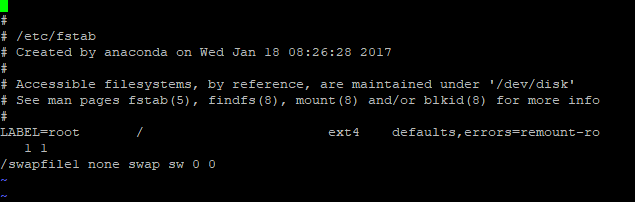
Using escape colon wq, save the file and close it.
How do I verify Linux swap file is activated or not?
Simply use the free command:
#free -m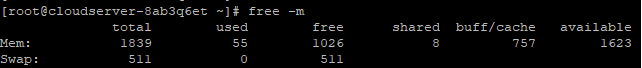
How can I display swap usage summary on Linux?
Type the following swapon command:
#swapon -s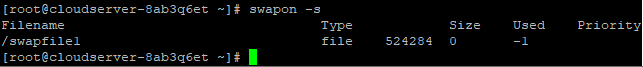
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have learned how to add a swap file in linux.
Also read: How to prevent a user from login in Linux
Thank You 🙂