Assign and Upadte public IP
Utho’s network configuration allows users to manage various network settings for their cloud instances, including public and private IP addresses and VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) assignments. This section provides detailed information on how to manage these network settings effectively.
IPv4 Public IP Address
In this section, users can view all public networks associated with their cloud instance. The information is displayed in a table format, including the following details for each public network: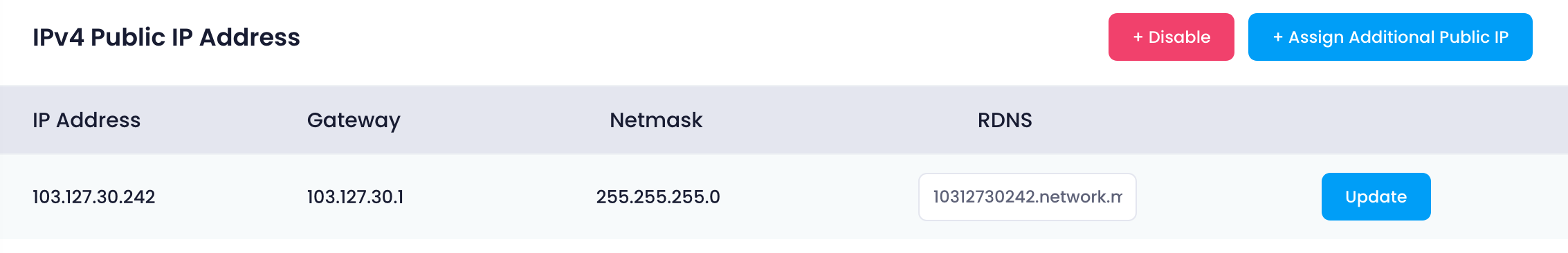
- IP Address : The public IP address assigned to the cloud instance.
- Gateway : The gateway for the public network, which routes traffic between the cloud instance and other networks. A Gateway is a network device or router that acts as the entry or exit point between two networks (e.g., between a local network and the internet). In cloud networking, the default gateway connects your instances to external networks, like the internet. It is essential for directing traffic between private cloud resources and the public internet or other external systems.
- Netmask : The subnet mask for the public network, defining the network’s IP range. A Netmask (or subnet mask) defines the range of IP addresses that belong to a specific subnet in a network. It determines which part of an IP address refers to the network and which part refers to the host. In cloud environments, the netmask is used to partition network resources and control IP address allocation within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
- RDNS is the process of resolving an IP address back to its associated domain name. Unlike DNS, which maps domain names to IP addresses, DNS maps IP addresses to domain names. In the cloud, rDNS is used for identifying the source of traffic and improving security (e.g., anti-spam measures). It helps verify that the server sending requests is authorized, enhancing trust and reducing the likelihood of malicious activity.For each public network, users have the following options:
- Update : Allows users to update the RDNS (reverse DNS) settings. Reverse DNS translates an IP address back to a domain name, which can be important for email servers and network diagnostics.
- Delete : Allows users to delete the public network. Deleting a public network will remove the associated public IP address and its configurations from the cloud instance. Click this to remove the public network. A confirmation dialog will appear to prevent accidental deletions.
- Enable/Disable : Allows users to enable or disable the public network. Disabling a network will temporarily deactivate the associated IP addresses.
- Enable/Disable Toggle: Use this switch to turn the public network on or off.
Additionally, there is a button to add an additional public IP address to the cloud instance:
- Add Additional Public IP : Click this button to allocate a new public IP address to your cloud instance. This will open a form where you can specify the new IP address details.
- Assigning an additional public IP in the cloud offers benefits like high availability through load balancing and scalability for handling more traffic. It allows service separation , enabling different services to have distinct IPs. Multiple IPs also improve redundancy and failover by providing alternative routes in case of failure. This setup enhances security by enabling specific firewall rules and access controls for each IP. Overall, it ensures better performance, reliability, and control over cloud resources.
IPv4 Private IP Address
In this section, users can view the private networks associated with their cloud instance. Private networks are used for internal communication within the data center and are not accessible from the public internet. The table displays:
- IP Address : The private IP address assigned to the cloud instance.
- Netmask : The subnet mask for the private network.
- Gateway : The gateway for the private network.
For each private network, there is an option to delete it:
- Delete : Allows users to delete the private network. Deleting a private network will remove the associated private IP address and its configurations from the cloud instance.