Add-nodepool
This guide demonstrates how to use the Utho API to add nodepool to the existing Kubernetes cluster and manage it programmatically. The example code snippets are provided in multiple programming languages, including cURL , Python , JavaScript (Node.js) , PHP , and Java .
API Endpoint
URL : https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/<cluster_id>/nodepool/add
Method : POST
Content-Type : application/json
Headers:
- Authorization:
Bearer YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN
Replace <cluster_id> with the ID of your existing Kubernetes cluster.
Request Payload
The payload structure is as follows:
{
"nodepools": [
{
"label": "pool-S6PbOW6b",
"size": "10215",
"count": "1",
"ebs": [
{
"disk": "30",
"type": "nvme"
}
]
}
]
}Example Code Snippets
Using Python (requests library)
import requests
import json
url = "https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/750031/nodepool/add"
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
data = {
"nodepools": [
{
"label": "pool-S6PbOW6b",
"size": "10215",
"count": "1",
"ebs": [
{
"disk": "30",
"type": "nvme"
}
]
}
]
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(response.json())JavaScript (Node.js with Axios)
const axios = require('axios');
const url = 'https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/750031/nodepool/add';
const headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer <your_api_token>',
};
const payload = {
nodepools: [
{
label: 'pool-S6PbOW6b',
size: '10215',
count: '1',
ebs: [
{ disk: '30', type: 'nvme' },
],
},
],
};
axios.post(url, payload, { headers })
.then(response => {
console.log('Response:', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error:', error.response.data || error.message);
});PHP (cURL)
<?php
$url = 'https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/750031/nodepool/add';
$headers = [
'Content-Type: application/json',
'Authorization: Bearer <your_api_token>',
];
$payload = [
'nodepools' => [
[
'label' => 'pool-S6PbOW6b',
'size' => '10215',
'count' => '1',
'ebs' => [
['disk' => '30', 'type' => 'nvme'],
],
],
],
];
$ch = curl_init($url);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
if ($response) {
echo "Response: " . $response;
} else {
echo "Error: " . curl_error($ch);
}Bash (cURL)
#!/bin/bash
url="https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/750031/nodepool/add"
token="<your_api_token>"
payload='{
"nodepools": [
{
"label": "pool-S6PbOW6b",
"size": "10215",
"count": "1",
"ebs": [
{"disk": "30", "type": "nvme"}
]
}
]
}'
response=$(curl -s -X POST "$url" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $token" \
-d "$payload")
echo "Response: $response"API Responses
Create Kubernetes Cluster
On success:
{
"status": "success",
"message": "Kubernetes Cluster deployment is in process and should be completed in few seconds.",
"id": 750063
}Add Node Pool
On success:
{
"status": "success",
"message": "New Node Pool added to cluster and a progress started to add nodes to the cluster.",
"id": "750031"
}Notes
- Ensure the payload values match your desired cluster configuration.
- Replace placeholder values like
dcslug,vpc,nodepools, andcluster_idas per your requirements. - Proper error handling should be implemented in your application for production usage.
Adding a Node Pool to Cluster using Control Panel
1. Navigate to the Cluster Dashboard
- Log in to your Utho Cloud account.
- Go to the Kubernetes section.
- Select the cluster to which you want to add a node pool.
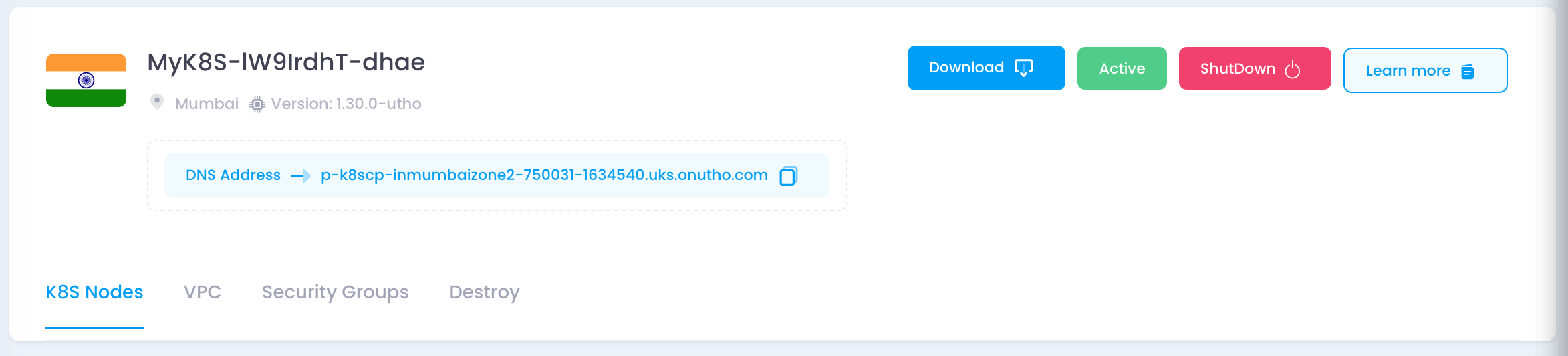
2. Open the Node Pool Management Section
- Scroll down to the Manage Node Worker Pools section.
- Click the + Add Node Pool button.

3. Configure the Node Pool
- A Pool Worker configuration window will appear.
- The system will generate a default pool name (e.g.,
pool-S6PbOW6b). You can modify it if needed. - Select the Node Size by clicking the Select Node Size button.
- Adjust the Desired Count of nodes using the
+or-buttons. - Review the Total Cost displayed at the bottom.
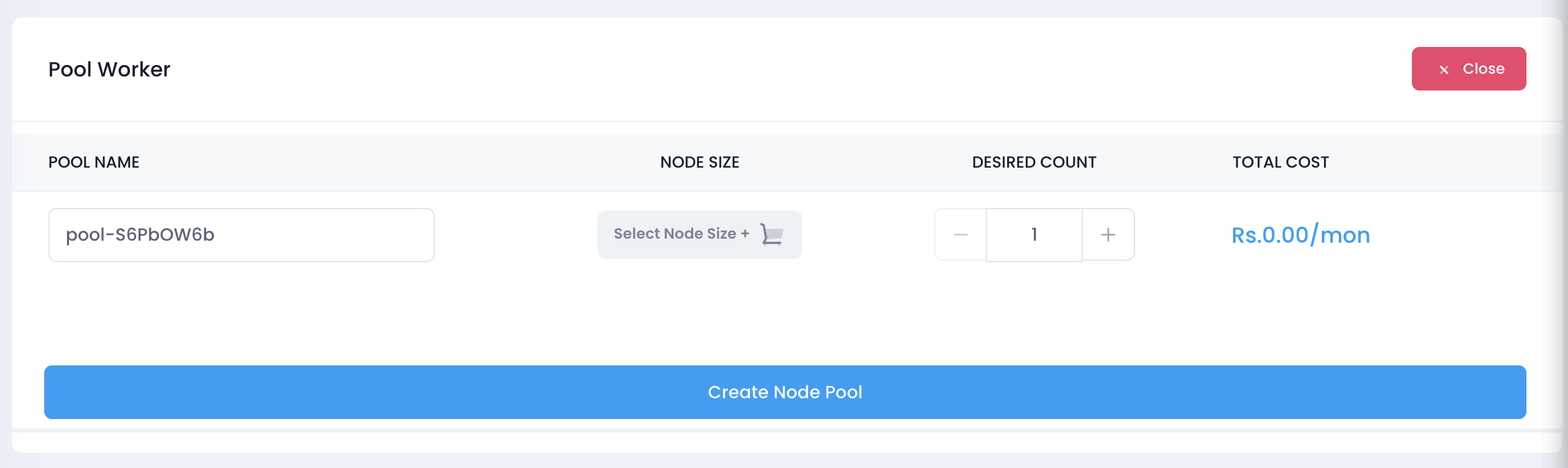
4. Create the Node Pool
- Once all configurations are set, click the Create Node Pool button.
- The system will initiate the creation process.
- Wait for the process to complete and verify the node pool appears in the cluster’s node list.
Verify if a Node Pool is Added to the Kubernetes Cluster
- Go back to the K8S Nodes tab.
- Ensure that the newly added node pool is listed and in an active state.
Once you have added a node pool to your cluster, follow these steps to confirm its successful addition:
Step 1: Check Available Nodes
Run the following command to list all nodes in the cluster:
kubectl get nodes -o wide- If the newly added nodes appear in the output, the node pool has been successfully added.
- You can check the AGE column to distinguish newly added nodes.
Step 2: Verify Node Labels
Each node pool may have specific labels. To check if the nodes belong to the new node pool:
kubectl get nodes --show-labels- Look for labels such as
nodepool=<your-nodepool-name>.
Alternatively, filter nodes by a specific label:
kubectl get nodes -l nodepool=<your-nodepool-name>Step 3: Describe a Node
Pick a node from the new node pool and describe it:
kubectl describe node <node-name>- This will show details such as node capacity, conditions, and taints.
Step 4: Check Running Pods on New Nodes
To verify if workloads are scheduled on the new nodes:
kubectl get pods -o wide- Check the NODE column to see if new nodes are hosting pods.
If no pods are scheduled, you can try deploying a test workload targeting the new node pool.
Step 5: Deploy a Test Pod to New Node Pool (Optional)
If you want to ensure that new nodes are being utilized, create a pod specifically scheduled on the new node pool:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod
spec:
nodeSelector:
nodepool: <your-nodepool-name>
containers:
- name: test-container
image: nginxApply it using:
kubectl apply -f test-pod.yaml
kubectl get pods -o wideIf the pod runs successfully on a node from the new node pool, it confirms the addition.
Step 6: Check Autoscaler (If Enabled)
If your cluster has an autoscaler enabled, ensure that the new node pool is registered correctly:
kubectl get configmap -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler-status -o yamlLook for the node pool in the status.