Create-cluster
Follow these steps to deploy a Kubernetes cluster on Utho Cloud platform using the Kubernetes deployment page.
How to Create a Kubernetes Cluster using Utho API
This guide demonstrates how to use the Utho API to create a Kubernetes cluster programmatically. The example code snippets are provided in multiple programming languages, including cURL , Python , JavaScript (Node.js) , PHP , and Java .
API Endpoint
URL : https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/deploy
Method : POST
Content-Type : application/json
Headers:
- Authorization:
Bearer YOUR_BEARER_TOKEN
Request Payload
The payload structure is as follows:
{
"dcslug": "inmumbaizone2",
"cluster_label": "MyK8S-z2tkradY-wkjp",
"cluster_version": "1.30.0-utho",
"nodepools": [
{
"label": "pool-Kcpvcjdg",
"size": "10045",
"count": "1",
"maxCount": "1"
}
],
"vpc": "1c689760-e9cf-48e3-b62d-8128b5e6edd7",
"subnetRequired": "false",
"network_type": "public",
"firewall": "on",
"cpumodel": "amd"
}Example Code Snippets
1. Using cURL
curl -X POST https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/deploy \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"dcslug": "inmumbaizone2",
"cluster_label": "MyK8S-z2tkradY-wkjp",
"cluster_version": "1.30.0-utho",
"nodepools": [
{
"label": "pool-Kcpvcjdg",
"size": "10045",
"count": "1",
"maxCount": "1"
}
],
"vpc": "1c689760-e9cf-48e3-b62d-8128b5e6edd7",
"subnetRequired": "false",
"network_type": "public",
"firewall": "on",
"cpumodel": "amd"
}'2. Using Python (requests library)
import requests
import json
url = "https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/deploy"
headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
data = {
"dcslug": "inmumbaizone2",
"cluster_label": "MyK8S-z2tkradY-wkjp",
"cluster_version": "1.30.0-utho",
"nodepools": [
{
"label": "pool-Kcpvcjdg",
"size": "10045",
"count": "1",
"maxCount": "1"
}
],
"vpc": "1c689760-e9cf-48e3-b62d-8128b5e6edd7",
"subnetRequired": "false",
"network_type": "public",
"firewall": "on",
"cpumodel": "amd"
}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
print(response.json())3. Using JavaScript (Node.js - Axios)
const axios = require('axios');
const url = 'https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/deploy';
const headers = {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
};
const data = {
dcslug: "inmumbaizone2",
cluster_label: "MyK8S-z2tkradY-wkjp",
cluster_version: "1.30.0-utho",
nodepools: [
{
label: "pool-Kcpvcjdg",
size: "10045",
count: "1",
maxCount: "1"
}
],
vpc: "1c689760-e9cf-48e3-b62d-8128b5e6edd7",
subnetRequired: "false",
network_type: "public",
firewall: "on",
cpumodel: "amd"
};
axios.post(url, data, { headers: headers })
.then(response => console.log(response.data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));4. Using PHP (cURL)
<?php
$url = "https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/deploy";
$headers = [
"Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type: application/json"
];
$data = [
"dcslug" => "inmumbaizone2",
"cluster_label" => "MyK8S-z2tkradY-wkjp",
"cluster_version" => "1.30.0-utho",
"nodepools" => [
[
"label" => "pool-Kcpvcjdg",
"size" => "10045",
"count" => "1",
"maxCount" => "1"
]
],
"vpc" => "1c689760-e9cf-48e3-b62d-8128b5e6edd7",
"subnetRequired" => "false",
"network_type" => "public",
"firewall" => "on",
"cpumodel" => "amd"
];
$ch = curl_init($url);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, 1);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($data));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
echo $response;5. Using Java (HttpURLConnection)
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class KubernetesCluster {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String url = "https://api.utho.com/v2/kubernetes/deploy";
String jsonInputString = "{\"dcslug\":\"inmumbaizone2\",\"cluster_label\":\"MyK8S-z2tkradY-wkjp\",\"cluster_version\":\"1.30.0-utho\",\"nodepools\":[{\"label\":\"pool-Kcpvcjdg\",\"size\":\"10045\",\"count\":\"1\",\"maxCount\":\"1\"}],\"vpc\":\"1c689760-e9cf-48e3-b62d-8128b5e6edd7\",\"subnetRequired\":\"false\",\"network_type\":\"public\",\"firewall\":\"on\",\"cpumodel\":\"amd\"}";
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) new URL(url).openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json", "Authorization", "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY");
conn.setDoOutput(true);
try (OutputStream os = conn.getOutputStream()) {
byte[] input = jsonInputString.getBytes("utf-8");
os.write(input, 0, input.length);
}
int code = conn.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("Response Code: " + code);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Response
On success, the API returns a response like this:
{
"status": "success",
"message": "Kubernetes Cluster deployment is in process and should be completed in few seconds.",
"id": 750063
}Notes
- Ensure the payload values match your desired cluster configuration.
- Replace placeholder values like
dcslug,vpc, andnodepoolsas per your requirements. - Proper error handling should be implemented in your application for production usage.
This guide provides a foundation for integrating Utho API into your system.
Create a Kubernetes Cluster using Control Panel
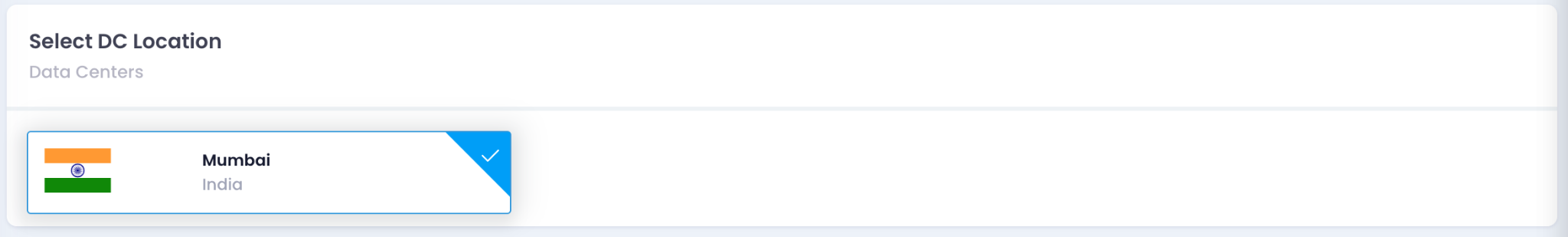
1. Select DC Location
- Choose a Data Center location from the dropdown menu.
- Example: Select “Mumbai, India.”
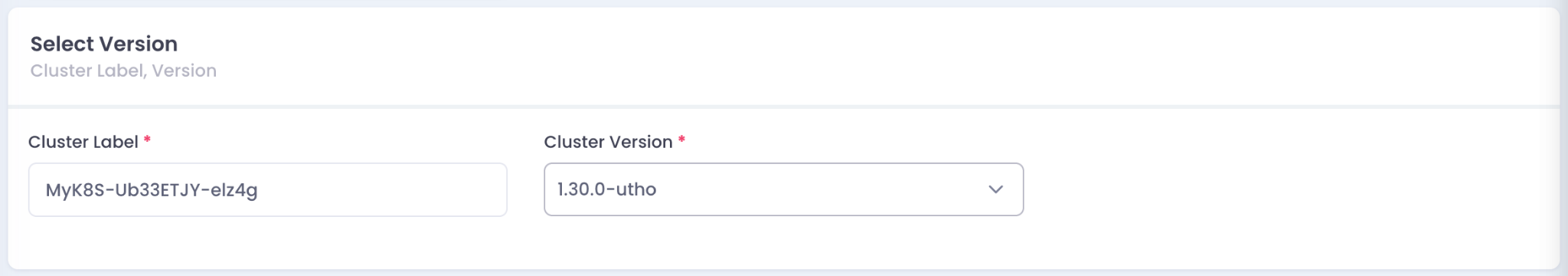
2. Select Kubernetes Version
- Enter a Cluster Label to identify your Kubernetes cluster.
- Choose a Cluster Version from the dropdown menu.
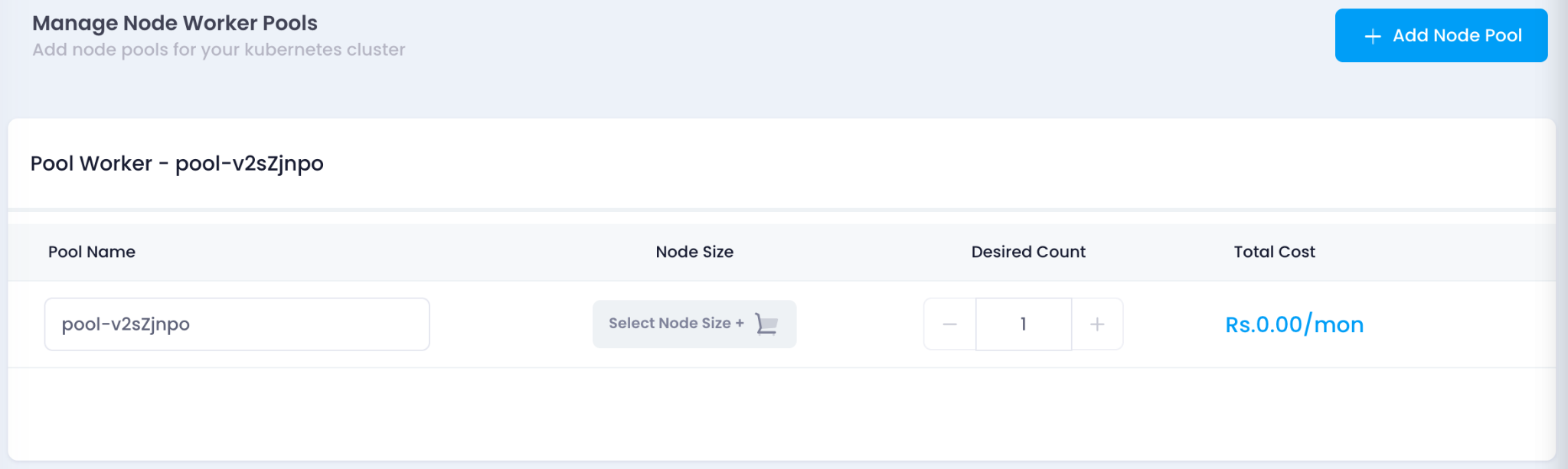
3. Manage Node Worker Pools
- Click on Add Node Pool to configure worker nodes for the cluster.
- Provide a Pool Name for the node pool.
- Select a Node Size from the dropdown menu to allocate resources for the nodes.
- Specify the Desired Count of nodes in the node pool.
- The Total Cost will be calculated automatically based on the configuration.
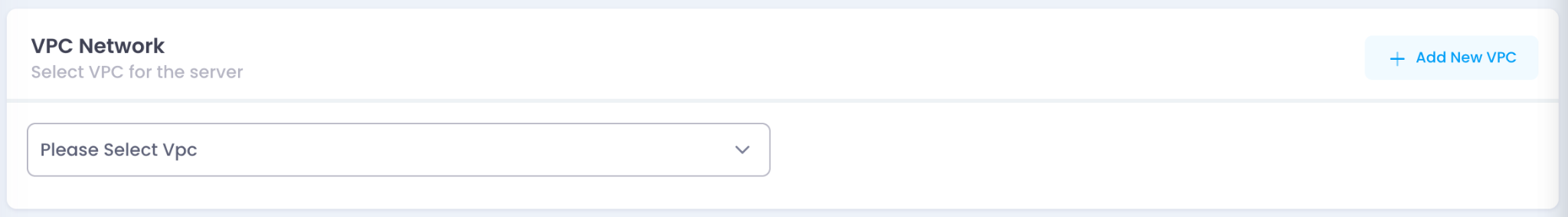
4. Configure VPC Network
- Select an existing VPC Network or click Add New VPC to create a new one.
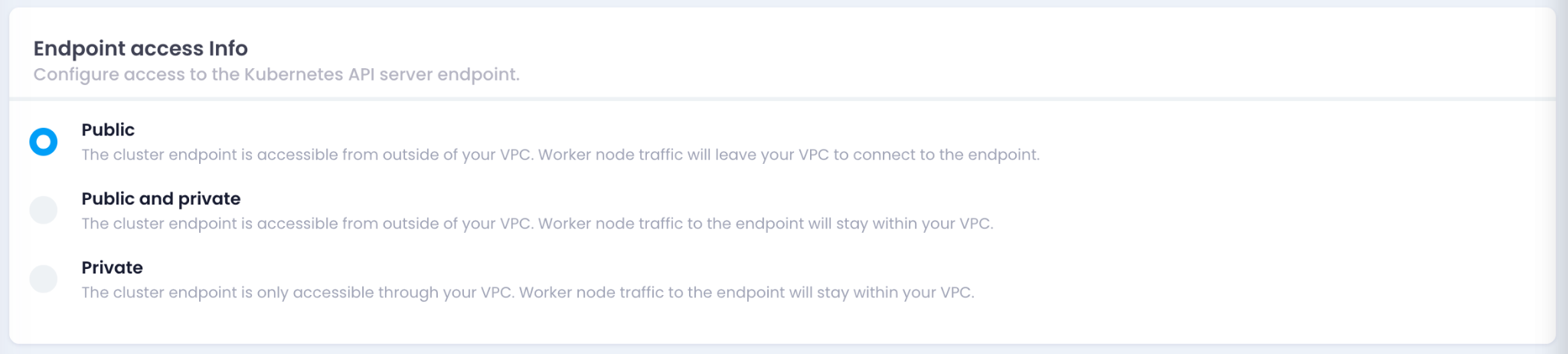
5. Configure Endpoint Access Info
- Choose the endpoint access level for the Kubernetes API server:
- Public : Accessible from outside the VPC.
- Public and Private : Accessible from both outside and within the VPC.
- Private : Accessible only within the VPC.
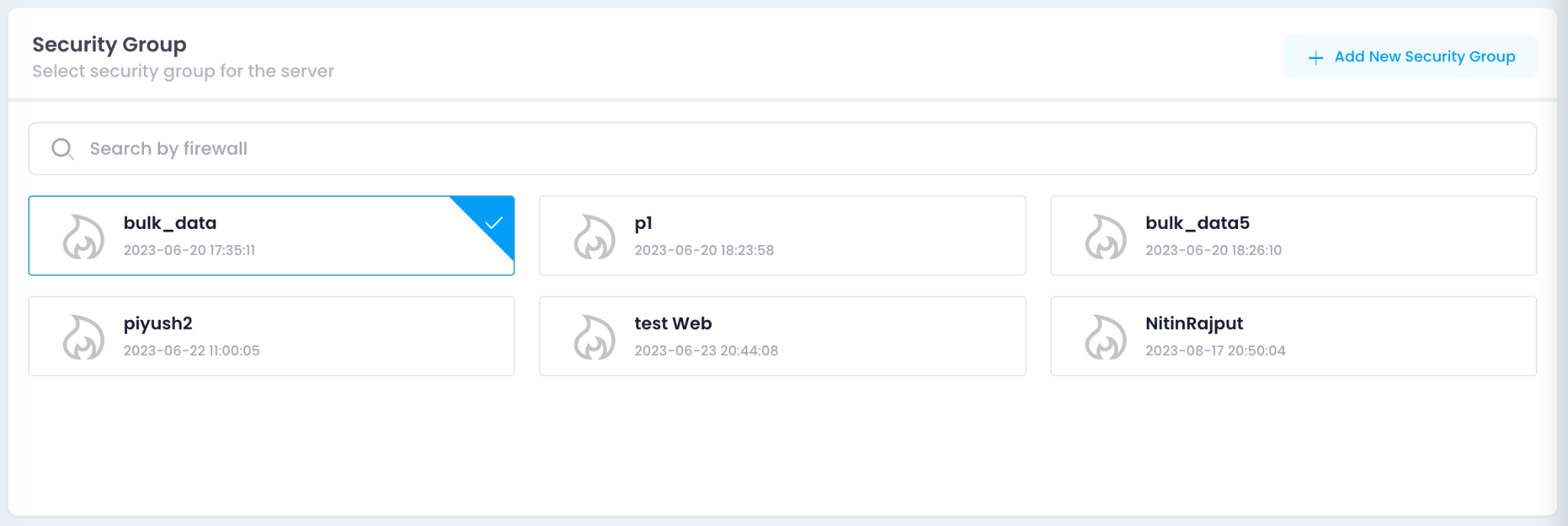
6. Configure Security Group
- Select a Security Group from the available options or click Add New Security Group to create a new one.
8. Deploy the Cluster
- Review the total cost displayed at the bottom.
- Click Deploy Cluster to initiate the deployment process.

9. Verify the Cluster Deployment
Once the Kubernetes cluster deployment reaches 100%, you need to verify that the cluster is running correctly.
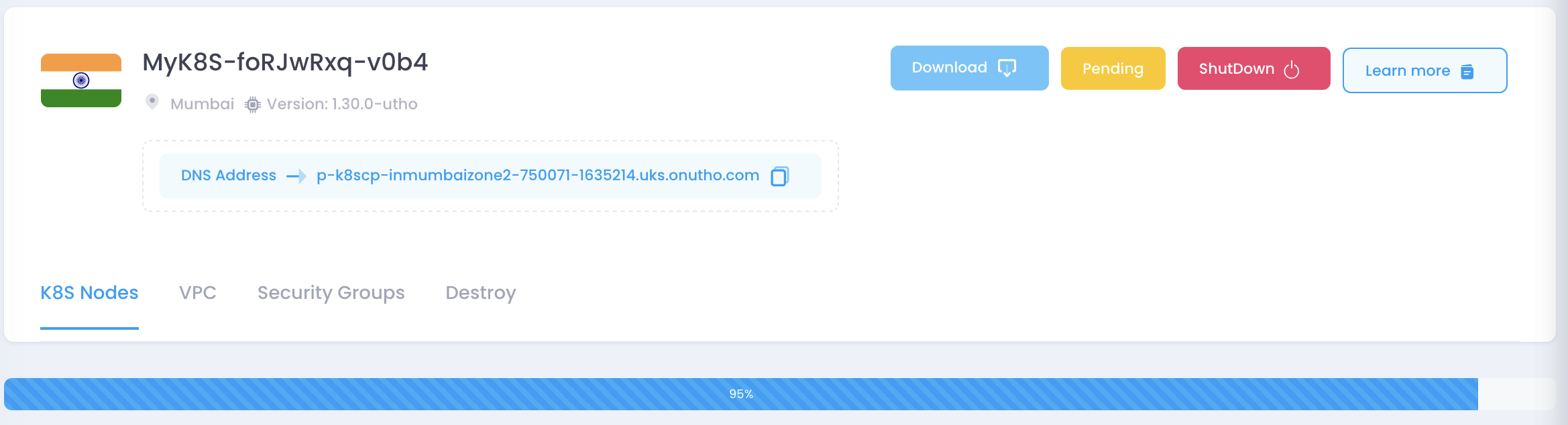
Steps to verify:
Check Cluster Status
Download the Kubeconfig file by clicking the “Download” button in the UI.
Access the Cluster
Set the environment variable for the Kubeconfig file and check cluster details:
export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/your/kubeconfig.yaml kubectl cluster-infoList Nodes
Ensure the nodes are correctly added to the cluster:
kubectl get nodesCheck Running Pods
Verify that all system pods are running:
kubectl get pods -ADeploy a Test Application (Optional)
Deploy a simple Nginx pod to test:
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx kubectl get pods
Once these checks confirm a properly running cluster, the deployment verification is complete. Let me know if you need modifications!