Python will be very popular in 2026. It is used for AI systems cloud automation building APIs and handling data.
Because many people use Python, interviews have become harder and more practical.
Whether you are a beginner, a mid-level developer, a QA engineer or a senior engineer this guide will help you learn all the important Python concepts.
In this comprehensive resource, you will find:
- 50+ fully explained Python interview questions
- Conceptual, theory, and practical coding questions
- Multiple python practice questions
- Hands-on python coding practice problems
- Real-world python coding problems and solutions
- Separate sections for freshers and experienced professionals
This guide is made to help with interviews at companies like Google Microsoft Meta Netflix Paytm Swiggy Zoho and more. These companies ask Python questions to check problem-solving skills, coding style, clear thinking and understanding of software design.
Section 1: Why Python Interviews Matter in 2026
Python is not just a simple coding language today. It is used to build modern software. With AI cloud automation and data science growing Python has become the main choice for developers.
✔ Why Python Is Critical for Modern Tech Roles
Python remains the industry favorite because of:
- Clean & readable syntax
- Huge library ecosystem (NumPy, Pandas, FastAPI, Django, TensorFlow, etc.)
- Cross-platform support
- Fast development cycles
- Strong community support
✔ Python Powers Almost Every Modern Tech Domain
Today, Python is deeply integrated into:
- Backend development
- Cloud & DevOps automation
- Cybersecurity scripting
- Machine learning & AI
- Data analytics pipelines
- Test automation frameworks
- API and microservices architecture
This is why companies like Google, Microsoft, Netflix, Paytm, Zoom, and Meta extensively rely on python interview questions during hiring rounds to test:
- Logical reasoning
- Real-world coding skills
- Code optimization
- API design thinking
- Debugging and troubleshooting
- Problem-solving approach
Modern hiring demands not only theory but also hands-on python coding practice and the ability to solve python coding problems and solutions under time pressure.
This guide merges theory + practical knowledge to help you stand out in all interview rounds.
Section 2: Python Basics — Top 20 Python Basic Interview Questions
The following are the most important python basic interview questions frequently asked in fresher-level and junior developer interviews in 2026.
These ensure you have a strong foundation before moving to advanced topics.
Q1. What is Python? Why is it so popular?
Python is a high-level programming language. It is easy to read simple to use and helps people work faster. Python is used in AI machine learning automation data science backend coding cloud work DevOps security and web applications.
Why is Python so popular in 2026?
Python is popular because it is strong and easy to use.
- Extremely Easy to Learn and Use
Python code is almost like English. Beginners can quickly understand how programming works. This is why many python basic interview questions start with simple topics like variables loops and data types.
2. Huge Ecosystem of Libraries and Frameworks
Python offers massive libraries like:
- NumPy, Pandas → Data analysis
- TensorFlow, PyTorch → Machine learning
- Django, Flask, FastAPI → Backend development
- Boto3, Fabric → Cloud automation
- Selenium, PyTest → Automation testing
This makes Python ideal not just for developers but also for testers, data scientists, and cloud engineers.
- Cross-Platform and Works Anywhere
Python can run on Linux Windows macOS Android and small devices. This makes it very flexible to use in real life. - Strong Community and Company Support
Companies like Google Microsoft Amazon Meta Netflix use Python a lot. This means Python will keep getting updates and new features. - Good for Automation and Fast Development
Python is used to write scripts for repeated tasks in DevOps AI and other work. It helps finish work quickly.
Because of these reasons the question What is Python is one of the most common python interview questions. It is often asked for both beginners and experienced Python roles.
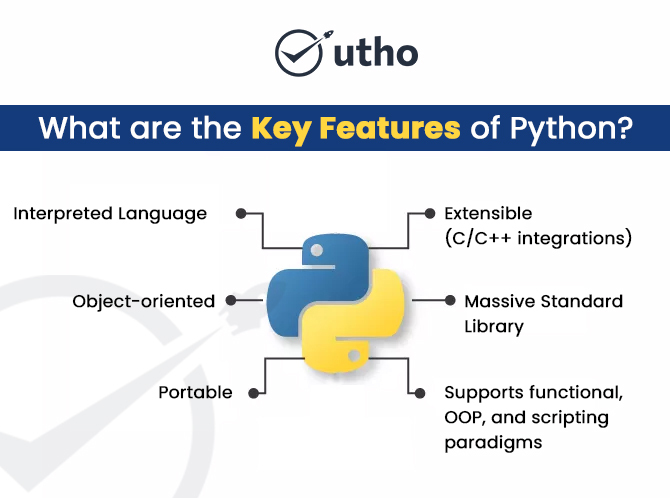
Q2. What are the Key Features of Python?
Python stands out due to several powerful features that make development faster and more efficient.
1. Interpreted Language
Python code is executed line-by-line using the CPython interpreter.
This feature makes debugging simpler and is why Python is preferred in python coding practice and python practice questions used in companies.
2. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Python supports:
- Classes
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Encapsulation
Yet it maintains flexibility to be used as a procedural or functional programming language as well.
3. Portable and Cross-Platform
Write code once, run it anywhere — without modification. This is a major benefit in multi-environment development environments like cloud, DevOps, and distributed systems.
4. Highly Scalable and Extensible
Python can integrate with:
- C/C++ for performance
- Java (via Jython)
- .NET (via IronPython)
This hybrid flexibility allows developers to build scalable applications used in production at companies like Instagram and Dropbox.
5. Huge Standard Library
Python includes a “batteries included” philosophy. The standard library provides modules for:
- OS operations
- File handling
- Networking
- Regex
- Database handling
- Testing
- Encryption
- JSON processing
This reduces dependency on third-party tools—one reason Python dominates automation-based python coding problems and solutions.
6. Support for Multiple Programming Paradigms
Python supports:
- Functional programming
- Object-oriented programming
- Scripting
- Modular programming
This versatility is a major factor interviewers test through python programming questions and answers.
This question appears regularly in python interview questions for freshers because it checks conceptual understanding rather than syntax knowledge.
Q3. What is PEP 8? Why is it Important?
PEP 8 (Python Enhancement Proposal 8) is the official style guide for writing clean and readable Python code. It defines formatting rules for:
- Indentation
- Variable naming conventions
- Line length
- Code structure
- Spacing
- Comments and documentation
- Best practices for import statements
Why is PEP 8 important?
Companies expect Python developers to write clean, scalable, and maintainable code. In real python coding practice rounds, messy code—even if correct—reduces scores.
What PEP 8 Improves:
✔ Readability
Helps teams understand code easily.
✔ Consistency
Standard style across large projects.
✔ Professionalism
Shows discipline and coding maturity.
✔ Debugging and Collaboration
Code that follows PEP 8 is easier to debug, modify, and maintain.
Example: PEP 8 Compliant Code
def calculate_total(price, tax):
total = price + (price * tax)
return total
Interviewers often ask PEP 8 questions in:
- python interview questions for experienced
- python coding practice rounds
- python coding problems and solutions
Because they want to check whether you can write clean, industry-level code.
Q4. What are Lists and Tuples?
Lists and tuples are two important ways to store data in Python. They are used very often and appear in many python basic interview questions. They are also asked in python interview questions for freshers and for experienced Python jobs.
Both store ordered collections of elements, but they differ in behavior and performance.
Key Differences Between List and Tuple
| Feature | List | Tuple |
| Mutability | Mutable (elements can be changed) | Immutable (elements cannot be modified) |
| Syntax | [] | () |
| Performance | Slower due to mutability overhead | Faster because they are fixed |
| Use Case | When modification is required | When data must remain unchanged |
| Memory Usage | Uses more memory | Uses less memory |
Examples
List Example
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"]
fruits.append("orange") # Allowed
Tuple Example
user = ("Lalit", 27, "Developer")
# user[0] = "Amit" → Not allowed (immutable)
Where Lists and Tuples Are Used in Interviews?
- Lists appear in python coding practice problems like sorting, searching, merging, and iteration.
- Tuples appear in system design questions, function returns, and immutable data structures.
This is why this question is almost always included in python basic interview questions.
Q5. What is a Dictionary in Python?
A dictionary in Python is an unordered, mutable, and key-value pair data structure. It is one of the most powerful built-in types and is heavily used in real-world python coding problems and solutions.
Structure
- Keys → must be unique and immutable
- Values → can be any type
Example
user = {
"name": "Lalit",
"role": "Developer",
"experience": 3
}
Key Features
✔ Fast lookup (O(1) average time)
✔ Ideal for structured data
✔ Extensively used in APIs, JSON, configuration files, and backend applications
Why Dictionaries Are Important in Interviews
- JSON parsing uses dictionaries
- REST API data is dictionary-based
- Many python practice questions involve dictionary manipulation
Interviewers frequently test:
- Merging dictionaries
- Iterating through keys/values
- Using dict comprehensions
- Handling nested dictionaries
Q6. Explain Python Variables.
Variables in Python are names (identifiers) that reference objects stored in memory. Python uses dynamic typing, meaning you don’t need to declare the datatype explicitly.
Key Properties
✔ Dynamic Typing
x = 10
x = "Hello" # Allowed
✔ Object Reference Model
A variable does not store value directly — it stores a reference to an object in memory.
✔ No Type Declaration Required
name = "Lalit"
age = 25
salary = 75000.50
✔ Memory Allocation is Automatic
Python handles memory using:
- Reference counting
- Garbage collection
Why Interviewers Ask This Question
Understanding variables is essential for:
- python programming questions and answers
- debugging
- writing efficient code
- understanding mutability vs immutability
It is one of the most common python interview questions for freshers.
Q7. What is a Module in Python?
A module is simply a Python file (.py) that contains functions, classes, and variables which you can import and reuse in other programs.
Example: mymodule.py
def greet():
return "Hello from module"
Using the module
import mymodule
print(mymodule.greet())
Why Modules Matter
✔ They promote code reusability
✔ Help structure big projects
✔ Reduce repetition
✔ Used in every python coding practice exercise involving architecture
Modules are the building blocks of Python applications, which is why this appears frequently in python interview questions for experienced roles.
Q8. What is a Package in Python?
A package is a directory (folder) that contains multiple modules and includes an __init__.py file, which signals to Python that the directory should be treated as a package.
Folder Structure Example
myproject/
utils/
__init__.py
math_ops.py
string_ops.py
Purpose of Packages
- Organize large applications
- Group related modules
- Increase maintainability
Interview Tip
Packages appear in python programming questions and answers when dealing with:
- application architecture
- project structure
- modularity
Q9. Explain Python’s Indentation Rule.
Unlike most languages that use { } braces, Python uses indentation to define code blocks.
Example
if age > 18:
print("Adult")
else:
print("Minor")
The default indentation is 4 spaces, not tabs.
Why Indentation Matters
✔ Improves readability
✔ Prevents logical errors
✔ Makes code clean and consistent
✔ Ensures PEP 8 compliance
This is why indentation rules are heavily tested in python practice questions and python coding practice rounds.
Q10. What are Python Namespaces?
A namespace is a mapping between names (identifiers) and the objects they refer to.
Think of it as a container that holds names and helps avoid naming conflicts.
Types of Namespaces
- Local Namespace
Inside functions.
- Global Namespace
At the module level.
- Built-in Namespace
Contains built-in functions like print(), len().
Example
x = 10 # Global namespace
def func():
y = 20 # Local namespace
Why Namespaces Matter in Interviews
They are essential for understanding:
- variable scope
- memory management
- debugging
- closures
This question is frequently seen in python interview questions for experienced candidates.
Q11. What are *args and **kwargs in Python? (Deep Explanation)
In Python, *args and **kwargs allow you to pass a variable number of arguments to a function. They are essential for flexible function design and frequently appear in python interview questions for experienced roles.
1. *args (Non-Keyword Variable Arguments)
*args collects extra positional arguments into a tuple.
Example
def total(*numbers):
return sum(numbers)
print(total(10, 20, 30)) # Output: 60
2. **kwargs (Keyword Variable Arguments)
**kwargs collects extra keyword arguments into a dictionary.
Example
def user_info(**details):
return details
print(user_info(name="Lalit", age=28))
Why This Question is Important
- Used in decorators
- Used in class inheritance
- Used in API functions
- Appears in python practice questions and python programming questions and answers
Q12. What is Type Casting in Python?
Type casting means converting one datatype into another. Python supports explicit and implicit type conversion.
Explicit Type Casting
The programmer manually converts the type.
x = "10"
y = int(x)
Implicit Type Casting
Python automatically converts the type.
x = 10
y = 10.5
result = x + y # Result becomes float
Why Type Casting Matters
- Used heavily in python coding practice
- Important for input handling
- Required in mathematical and data science programs
Q13. Difference Between remove(), pop(), and del?
These are common operations for modifying lists and are frequently asked in python basic interview questions.
| Method | Purpose | Example |
| remove() | Removes the first matching value | lst.remove(5) |
| pop() | Removes item by index and returns it | lst.pop(2) |
| del | Deletes index, slice, or entire object | del lst[1], del lst |
Example
lst = [10, 20, 30, 40]
lst.remove(20) # removes the value 20
lst.pop(1) # removes item at index 1
del lst[0] # deletes first element
Interview Tip
pop() is the only one that returns the removed element — useful in python coding problems and solutions.
Q14. What is a Lambda Function?
A lambda function is a small, anonymous, inline function defined using the lambda keyword.
Syntax
lambda arguments: expression
Example
square = lambda x: x*x
print(square(5)) # Output: 25
Where Lambda Functions Are Used
- Sorting
- Filtering
- Map/Reduce operations
- Functional programming
- Interview coding tasks
They appear in many python programming questions and answers because they make code compact and expressive.
Q15. What is the Difference Between append() and extend()?
These are common list methods that behave differently.
append()
Adds one element to the list.
lst = [1, 2, 3]
lst.append([4, 5])
# Result: [1, 2, 3, [4, 5]]
extend()
Adds each element of an iterable to the list.
lst = [1, 2, 3]
lst.extend([4, 5])
# Result: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Why Interviewers Ask This
Misuse of append() and extend() is common among beginners, making this a high-frequency python basic interview question.
Q16. Explain List Comprehension.
List comprehension is a concise and efficient way to build new lists. It is widely tested in python coding practice and python practice questions.
Syntax
[expression for item in iterable if condition]
Example
squares = [x*x for x in range(10)]
Why It's Important
- Faster than loops
- Clean and readable
- Used in python coding problems and solutions involving data transformation
Q17. What is the pass Statement?
pass is a null statement in Python. It does nothing and is used as a placeholder when a statement is syntactically required.
Example
def future_function():
pass
Where pass is Used
- Empty loops
- Empty classes
- Skeleton code
- Prototyping
Interviewers ask this to check understanding of Python’s structure and indentation rules.
Q18. What is the Difference Between sort() and sorted()?
Both are used to sort elements, but they behave differently.
sort()
- Works only on lists
- Sorts the list in-place
- Returns None
numbers = [3, 1, 4]
numbers.sort()
sorted()
- Works on any iterable
- Returns a new sorted list
- Original data remains unchanged
result = sorted([3, 1, 4])
In Interviews
Used in python programming questions and answers involving:
- Sorting algorithms
- Comparators
- Custom sorting using key functions
Q19. What is Slicing in Python?
Slicing allows you to extract sub-parts of lists, strings, tuples, and other sequences.
Syntax
sequence[start:stop:step]
Example
text = "PythonInterview"
print(text[0:6]) # Output: Python
print(text[::-1]) # Reverse string
Importance in Interviews
Common in:
- string manipulation questions
- array-based problems
- python coding practice rounds
Q20. What is the Use of init() in Python?
__init__() is a constructor method in Python used to initialize object attributes when an object is created.
Example
class User:
def __init__(self, name, role):
self.name = name
self.role = role
u = User("Lalit", "Developer")
Why It's Important
- Core part of OOP
- Used heavily in class-based interview questions
- Common in python interview questions for experienced
This completes the most frequently asked python basic interview questions.
Section 3: Top Python Interview Questions for Freshers (Deep Explanations)
These questions frequently appear in entry-level technical rounds at companies like Google, TCS, Infosys, Accenture, and Tech Mahindra. Each explanation below is presented in a clear, practical, and beginner-friendly manner.
Q21. What is the difference between Python 2 and Python 3? (Deep Explanation)
Python 2 and Python 3 are fundamentally different languages. Most modern companies now use Python 3, and understanding the differences is a common part of python interview questions for freshers.
Key Differences
| Feature | Python 2 | Python 3 |
| Print statement | print "Hello" | print("Hello") |
| Unicode | Text stored as ASCII | Strings are Unicode by default |
| Division | 5/2 → 2 (integer division) | 5/2 → 2.5 (true division) |
| Libraries | Many outdated | Modern, more powerful libraries |
| Future support | Discontinued in 2020 | Actively supported |
Why This Matters in Interviews
Companies expect developers to work with Python 3 because:
- Better performance
- Cleaner syntax
- Stronger security
- Modern library support for ML, AI, and automation
This makes it one of the most repeated python interview questions.
Q22. What are Python Data Types?
Python provides a rich set of built-in data types that form the foundation of python programming questions and answers during interviews.
Built-in Data Types
- int → integers
- float → decimal values
- str → strings
- list → ordered, mutable collections
- tuple → ordered, immutable collections
- dict → key-value mappings
- set → unordered unique elements
- complex → complex numbers (3+4j)
Why Data Types Are Important
Data types help Python determine:
- how values are stored
- what operations can be performed
- memory usage
Understanding data types is mandatory for python practice questions.
Q23. What is Mutability?
Mutability refers to whether an object’s value can change after it is created.
Mutable Objects
Can be modified in place:
- list
- dict
- set
lst = [1, 2]
lst.append(3) # Modified
Immutable Objects
Cannot be changed once created:
- tuple
- str
- int
- float
text = "hello"
# text[0] = "H" ❌ Not allowed
Why Interviewers Ask This
Mutability affects:
- memory usage
- performance
- thread safety
- function behavior
This appears in almost every set of python interview questions for freshers.
Q24. What is an Iterator?
An iterator is an object in Python that can be iterated (looped) one item at a time.
Requirements
An iterator must implement:
- __iter__()
- __next__()
Example
nums = iter([10, 20, 30])
print(next(nums)) # 10
print(next(nums)) # 20
Real-World Use
Iterators power:
- loops
- generators
- file reading
- data streaming
Interviewers use iterator questions to test fundamental Python comprehension.
Q25. What is a Generator?
A generator is a special function that returns values one at a time using the yield keyword instead of return.
Example
def generate_numbers():
for i in range(5):
yield i
Benefits
✔ Saves memory
✔ Faster than creating full lists
✔ Ideal for large datasets
Why This Appears in Interviews
Generators are widely used in:
- data pipelines
- machine learning
- streaming APIs
This makes it an essential concept in python coding practice.
Q26. What is the difference between local and global variables?
Local Variable
Declared inside a function
Available only inside that function
def func():
x = 5 # local variable
Global Variable
Declared outside functions
Can be accessed throughout the program
x = 10 # global variable
global Keyword
x = 100
def change():
global x
x = 200
Why Companies Ask This
It tests understanding of:
- variable scope
- memory management
- debugging
A common part of python interview questions for freshers.
Q27. What is Recursion?
Recursion occurs when a function calls itself until a base condition is reached.
Example
def factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
return n * factorial(n-1)
Important Concepts
- Base case
- Recursive case
- Stack memory
Where Recursion Appears in Interviews
Common in python coding practice involving:
- factorial
- Fibonacci
- tree traversal
- divide and conquer problems
Q28. Explain try-except-finally.
This is Python’s primary error-handling mechanism.
Structure
try:
# risky code
except Exception:
# handle error
finally:
# always executes
Purpose
- try → executes code
- except → catches exceptions
- finally → runs even if error occurs
Why It Matters
Handling exceptions is crucial for:
- file operations
- API requests
- database access
- automation scripts
Appears in python programming questions and answers for freshers and experienced engineers.
Q29. What is File Handling in Python?
File handling allows reading and writing data to external files.
Basic Functions
- open() → open file
- read() → read data
- write() → write data
- close() → close file
Example
with open("data.txt", "r") as f:
content = f.read()
File Modes
- "r" → read
- "w" → write
- "a" → append
- "rb" → read binary
Why Companies Test This
Used in:
- automation
- backend logs
- configuration loads
- data processing
A favorite topic in python practice questions.
Q30. What are Decorators in Python?
A decorator is a function that modifies or enhances another function without changing its actual code.
Example
def log(func):
def wrapper():
print("Function is running")
func()
return wrapper
@log
def greet():
print("Hello!")
Where Decorators Are Used
- Authentication
- Logging
- API rate limiting
- Performance measurement
Why It’s an Important Interview Topic
Decorators combine:
- functions
- closures
- higher-order logic
This question is frequently asked in python interview questions for freshers and intermediate developers.
Section 4: Top 20 Python Interview Questions for Experienced.
These advanced topics commonly appear in python interview questions for experienced, especially for roles involving backend systems, scalable architectures, automation, and distributed computing.
Q31. Explain GIL (Global Interpreter Lock).
The Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) is a mutex in CPython that ensures only one thread executes Python bytecode at any given time—even on multi-core processors.
It prevents memory corruption by making Python’s memory management thread-safe, but also limits parallel execution of CPU-bound threads.
Why GIL exists
- CPython uses reference counting for memory management.
- Modifying reference counters across threads might cause race conditions.
- The GIL simplifies implementation by serializing bytecode execution.
Impact on performance
- CPU-bound programs: Slower with threads due to GIL.
- I/O-bound programs: Threads work well because they frequently release GIL.
Workarounds
- Use multiprocessing to bypass GIL.
- Use C extensions or NumPy (which run outside GIL).
- Prefer asyncio for async I/O tasks.
GIL is always asked in python interview questions for experienced, especially for system design roles.
Q32. Difference between multiprocessing and multithreading?
| Feature | Multithreading | Multiprocessing |
| GIL impact | Threads blocked by GIL for CPU tasks | Each process has its own Python interpreter—no GIL |
| Memory | Shared | Independent |
| Best for | I/O-bound tasks | CPU-bound tasks |
| Performance | Lightweight; lower overhead | Higher overhead; true parallelism |
| Communication | Shared variables, queues | IPC, queues, pipes |
Summary
- Use multithreading for network requests, file handling, I/O waits.
- Use multiprocessing for ML models, number crunching, data processing pipelines.
This difference is heavily tested as part of python interview questions for experienced.
Q33. What are closures in Python?
A closure occurs when an inner function remembers and uses variables from the outer function, even after the outer function has finished executing.
Example
def outer(msg):
def inner():
print(msg)
return inner
f = outer("Hello")
f() # remembers msg even after outer ends
Why closures matter
- Used in decorators
- Enable data hiding
- Allow function factories
Closures are essential in python programming practice and functional-style coding.
Q34. What are Python descriptors?
Descriptors are objects that define how attributes are accessed in classes.
A descriptor must implement one or more of these methods:
- __get__(self, instance, owner)
- __set__(self, instance, value)
- __delete__(self, instance)
Use cases
- Implementing custom attribute access
- Validation (e.g., typed fields in frameworks)
- Property creation
- ORM field descriptors (like Django fields)
Example
class Value:
def __get__(self, obj, objtype):
return obj._value
def __set__(self, obj, val):
obj._value = val
class Test:
x = Value()
Descriptors are commonly asked in deep python interview questions for experienced.
Q35. Explain metaclasses.
A metaclass is the class of a class — meaning it defines how a class behaves.
Just like classes create objects, metaclasses create classes.
Use cases
- Enforcing coding standards
- Validating class attributes
- Creating frameworks (Django ORM uses metaclasses)
- Auto-registering classes in a registry
Example
class Meta(type):
def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs):
print("Creating class:", name)
return super().__new__(cls, name, bases, attrs)
class Test(metaclass=Meta):
pass
Metaclasses are a high-level concept and frequently appear in python interview questions for experienced engineers.
Q36. What is Monkey Patching?
Monkey patching means modifying code at runtime without altering the original source file.
Example
import math
math.sqrt = lambda x: "patched!"
print(math.sqrt(4))
Use cases
- Hotfixing functions dynamically
- Testing (mocking methods)
- Extending behavior of libraries not under your control
Risk
- Can break code unexpectedly
- Hard to debug
Because of its power and risk, it's a frequent topic in senior-level python interview questions.
Q37. What is memoization?
Memoization is a technique to speed up functions by caching previously computed results.
Why used?
- Saves time for repetitive function calls
- Optimizes recursive functions such as Fibonacci
Example
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=None)
def fib(n):
if n < 2:
return n
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
Memoization is very common in python coding practice, algorithm interviews, and performance optimization.
Q38. Explain async and await.
async and await enable asynchronous, non-blocking programming in Python.
Key concepts
- async function → returns a coroutine
- await → pauses execution until awaited task completes
- Uses an event loop
- Ideal for thousands of concurrent network operations
Example
import asyncio
async def task():
print("Start")
await asyncio.sleep(1)
print("End")
asyncio.run(task())
Async programming appears often in python interview questions for experienced relating to backend APIs.
Q39. What is the difference between deep copy and shallow copy?
| Type | Behavior |
| Shallow Copy | Copies only the outer object; inner objects share references |
| Deep Copy | Recursively copies everything, creating independent objects |
Example
import copy
shallow = copy.copy(obj)
deep = copy.deepcopy(obj)
Use case
Deep copy is used when modifying nested objects without affecting originals.
This is usually asked during python coding problems and solutions.
Q40. What is a context manager?
A context manager handles setup and teardown logic using __enter__() and __exit__().
Usage Example
with open("data.txt") as f:
content = f.read()
Why useful
- Manages resources safely
- Avoids memory leaks
- Closes files, DB connections, locks, sockets
Custom context manager example
class Manager:
def __enter__(self):
print("Start")
def __exit__(self, *args):
print("End")
with Manager():
pass
Context managers frequently appear in advanced python programming questions and answers.
Section 5: Important Python Coding Problems and Solutions (Top 15 — Deep Explanations)
This section covers real-world python coding problems and solutions frequently asked in technical interviews at companies like TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Accenture, Amazon, and startups.
These foundational challenges help you improve your python coding practice, especially for online assessments and onsite coding rounds.
Q41. Reverse a string without using slicing
Problem
Reverse a string without using Python’s slicing feature (s[::-1]).
Solution
def rev(s):
res = ""
for ch in s:
res = ch + res
return res
Explanation (Deep)
- We iterate through each character.
- Instead of appending at the end, we prepend each character to res.
- This builds the reversed string step-by-step.
Time Complexity:
O(n) — iterates through the string once.
This question repeatedly appears in python coding practice and beginner-level python programming questions and answers.
Q42. Check if a number is prime
Solution
def is_prime(n):
if n < 2:
return False
for i in range(2, int(n**0.5)+1):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True
Explanation (Deep)
- A prime number is divisible only by 1 and itself.
- We optimize by checking till square root of n, not the whole range.
- If any divisor is found, the number is not prime.
Time Complexity:
O(√n) — optimized for large input.
Prime-check problems are essential in python coding problems and solutions for freshers.
Q43. Find the factorial using recursion
Solution
def fact(n):
return 1 if n == 0 else n * fact(n-1)
Explanation (Deep)
- Uses the mathematical definition:
n! = n × (n−1)!
- Base case: factorial of 0 is 1.
- Recursive function calls reduce the problem size steadily.
Time Complexity:
O(n) due to recursion depth.
Factorial recursion is a classic in python programming questions and answers.
Q44. Count vowels in a string
Solution
sum(ch in "aeiou" for ch in s.lower())
Explanation (Deep)
- Convert the string to lowercase so checks are uniform.
- Use a generator expression to count matches.
- ch in "aeiou" returns True or False, and sum() converts them to integers.
Time Complexity:
O(n)
This lightweight approach appears often in python interview questions for freshers and python practice questions.
Q45. Find duplicates in a list
Solution
def dupes(lst):
seen = set()
return [x for x in lst if x in seen or seen.add(x)]
Explanation (Deep)
- Maintain a seen set.
- For each element:
- If already seen → it's a duplicate.
- If not → add to the set using seen.add(x).
- If already seen → it's a duplicate.
Why this works
set.add() returns None, which is considered False.
This clever trick helps detect duplicates in one pass.
Time Complexity:
O(n) — set operations are O(1).
A very common task in python coding practice.
Q46. Check if a string is palindrome
Solution
s == s[::-1]
Explanation (Deep)
A palindrome reads the same forwards and backwards.
Using slicing simplifies this drastically.
Time Complexity:
O(n)
Palindrome checks are very frequent in python basic interview questions.
Q47. Find the second largest number in a list
Solution
sorted(list(set(nums)))[-2]
Explanation (Deep)
- Convert list to set → removes duplicates.
- Sort values.
- Pick the second last element → second largest.
Edge Cases
- List with less than 2 unique numbers.
- Negative values.
- Mixed unsorted data.
Time Complexity:
O(n log n) due to sorting.
These types of ranking questions are part of many python programming questions and answers.
Q48. Generate Fibonacci series
Solution
def fib(n):
a, b = 0, 1
for _ in range(n):
print(a, end=" ")
a, b = b, a + b
Explanation (Deep)
The Fibonacci sequence starts with 0 and 1, and each next number is the sum of the previous two.
This iterative approach avoids recursion overhead.
Time Complexity:
O(n)
Fibonacci is a classic in python coding problems and solutions for logic testing.
Q49. Remove duplicates from a list while maintaining order
Solution
list(dict.fromkeys(lst))
Explanation (Deep)
- dict.fromkeys() removes duplicates while keeping insertion order.
- Converting dict keys back to a list gives the cleaned result.
Time Complexity:
O(n)
This trick is extremely popular in interview assessments and python coding practice.
Q50. Check if two strings are anagrams
Solution
sorted(a) == sorted(b)
Explanation (Deep)
- Two strings are anagrams if they contain the same characters in any order.
- Sorting both strings aligns characters, making comparison easy.
Time Complexity:
O(n log n) due to sorting.
Anagram checks frequently appear in both python basic interview questions and python coding problems and solutions.
Section 6: Expert-Level Python Practice Questions (15 Real Interview Problems)
This section focuses on expert-level python practice questions often seen in FAANG, top MNCs, fintech companies, and high-growth startups.
These questions help sharpen your logic, problem-solving skills, and understanding of Python internals—crucial for senior technical interviews and advanced python coding practice.
- Implement an LRU Cache
Building an LRU (Least Recently Used) cache tests your understanding of:
- HashMaps
- Doubly linked lists
- Time complexity optimization
Professional-level companies expect O(1) operations for both insert and retrieval.
- Rotate an Array by k Steps
Candidates should know the three recommended approaches:
- Using slicing
- Using a reverse algorithm
- Using modular arithmetic
This checks your mastery of arrays, indices, and algorithm optimization.
- Build Your Own map() Function
Implementing a custom map() tests:
- First-class functions
- Iterators
- Functional programming concepts
This is a favorite in python coding problems and solutions due to its simplicity yet conceptual depth.
- Merge Two Sorted Lists
A classic two-pointer problem.
Interviewers want to see clean logic and understanding of sorting strategies.
Often asked in python programming questions and answers for freshers and experienced.
- Convert JSON to a Python Class
Tests your knowledge of:
- json.loads()
- OOP concepts
- Dynamic attribute creation
Used frequently in backend and API-driven roles.
- Extract Domain Name from URL
This python practice question checks your ability to use:
- Regular expressions
- Python’s urllib module
- String manipulation
- Flatten Nested Lists
This can be solved using:
- Recursion
- Iterative stack
- Python generators
Interviewers test your ability to work with irregular data structures.
8. Implement Binary Search
A fundamental algorithm expected in any coding interview.
Candidates must implement both:
- Iterative version
- Recursive version
- Find the Top 3 Frequent Elements
Requires using:
- Dictionaries
- Sorting
- Heap (priority queue)
A common question for data-heavy roles in 2026.
- Validate Parentheses
Check your stack knowledge.
You must handle edge cases involving mismatched or incomplete brackets.
- Create a Custom Exception Class
Demonstrates your understanding of:
- Error handling
- Class inheritance
- Custom application flows
Senior Python roles frequently expect this knowledge.
- Remove Nth Node from End of a Linked List
Tests your knowledge of:
- Two-pointer technique
- Linked list traversal
- Edge case handling
- Convert List of Dicts into CSV
A practical task involving:
- File handling
- Python’s built-in csv module
- Data formatting logic
This appears in many python coding practice assessments.
- Build Your Own Decorator
This checks your understanding of:
- Closures
- Higher-order functions
- Wrapper functions
- Metadata preservation (functools.wraps)
Decorators are a fundamental concept in advanced Python development.
- Create a Generator That Yields Infinite Numbers
Tests generator internals:
- Lazy evaluation
- yield keyword
- Memory efficiency
A classic python practice question for automation engineers and data pipeline developers.
These 15 expert-level challenges help you master real-world python coding problems and solutions used in competitive hiring environments.
Section 7: Final Python Programming Questions and Answers (Advanced Mix — Deep)
This final section combines concept-heavy, reasoning-based python programming questions and answers asked during senior-level technical interviews in 2026.
Q51. What is Duck Typing? (Deep Explanation)
Duck Typing means the behavior of an object matters more than its actual type.
✔ If an object behaves like a list, Python treats it like a list.
✔ If it supports iteration, Python considers it iterable.
This aligns with Python’s philosophy:
“If it walks like a duck and quacks like a duck, it’s a duck.”
Why Do Interviewers Ask This?
To test understanding of Python’s dynamic typing, flexibility, and runtime behavior.
Highly common in python interview questions for experienced.
Q52. What is Pickling? (Deep Explanation)
Pickling is the process of serializing Python objects into bytes so they can be:
- Stored in files
- Transmitted over networks
- Cached
- Saved for later use
Python uses the pickle module for this.
Example:
import pickle
pickle.dump(obj, open("data.pkl", "wb"))
Why It Matters
Serialization is critical in:
- Machine learning model storage
- Distributed systems
- API communication
- Session management
Thus it appears frequently in python programming questions and answers.
Q53. What is a Virtual Environment? (Deep Explanation)
A Python virtual environment is an isolated workspace that contains:
- Its own Python interpreter
- Its own site-packages
- Its own dependency versions
You can have different environments for:
- Flask projects
- Django projects
- Data science notebooks
- Automation tools
Why It’s Important
It prevents dependency conflicts, allowing cleaner deployments and reproducible builds.
Q54. What is a REST API in Python? (Deep Explanation)
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for building scalable APIs.
In Python, REST APIs are commonly built using:
- Flask – lightweight, simple routing
- FastAPI – fastest Python framework, async-first
- Django REST Framework (DRF) – enterprise-grade architecture
Key Characteristics of REST APIs
✔ Stateless communication
✔ JSON input/output
✔ Use of HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
✔ Client–server separation
Why Interviewers Ask
REST APIs are essential for backend, cloud, DevOps, and microservice engineering roles in 2026.




