Base64 is one of those things every developer uses, but very few truly understand. You see Base64 strings everywhere - inside JWT tokens, API payloads, cookies, image previews, and even those long “secret-looking” strings you often copy–paste during integrations. It has become a universal way to safely transmit data across systems that were originally designed to handle only text.
But what exactly is Base64?
Why does it turn a normal string into a long, unreadable sequence of characters?
And how does JavaScript encode and decode it behind the scenes?
When you understand Base64 deeply, you also understand how browsers, servers, and APIs protect data from corruption during transport. Base64 isn’t encryption - it’s simply a smart way of representing binary data in a text-friendly format. And because JavaScript works heavily with text and binary buffers, knowing how Base64 works gives you better control over authentication, file uploads, security tokens, and data processing.
In this guide, we’ll break Base64 down in the simplest possible way:
- What Base64 actually does
- How encoding and decoding work internally
- Why web developers need it
- And the exact JavaScript methods to use - from btoa() and atob() to modern Buffer and TextEncoder APIs
By the end, you won’t just “use” Base64 - you’ll understand it like a pro.
1. What Is Base64 Encoding and Decoding?
1. Base64 in Simple Words
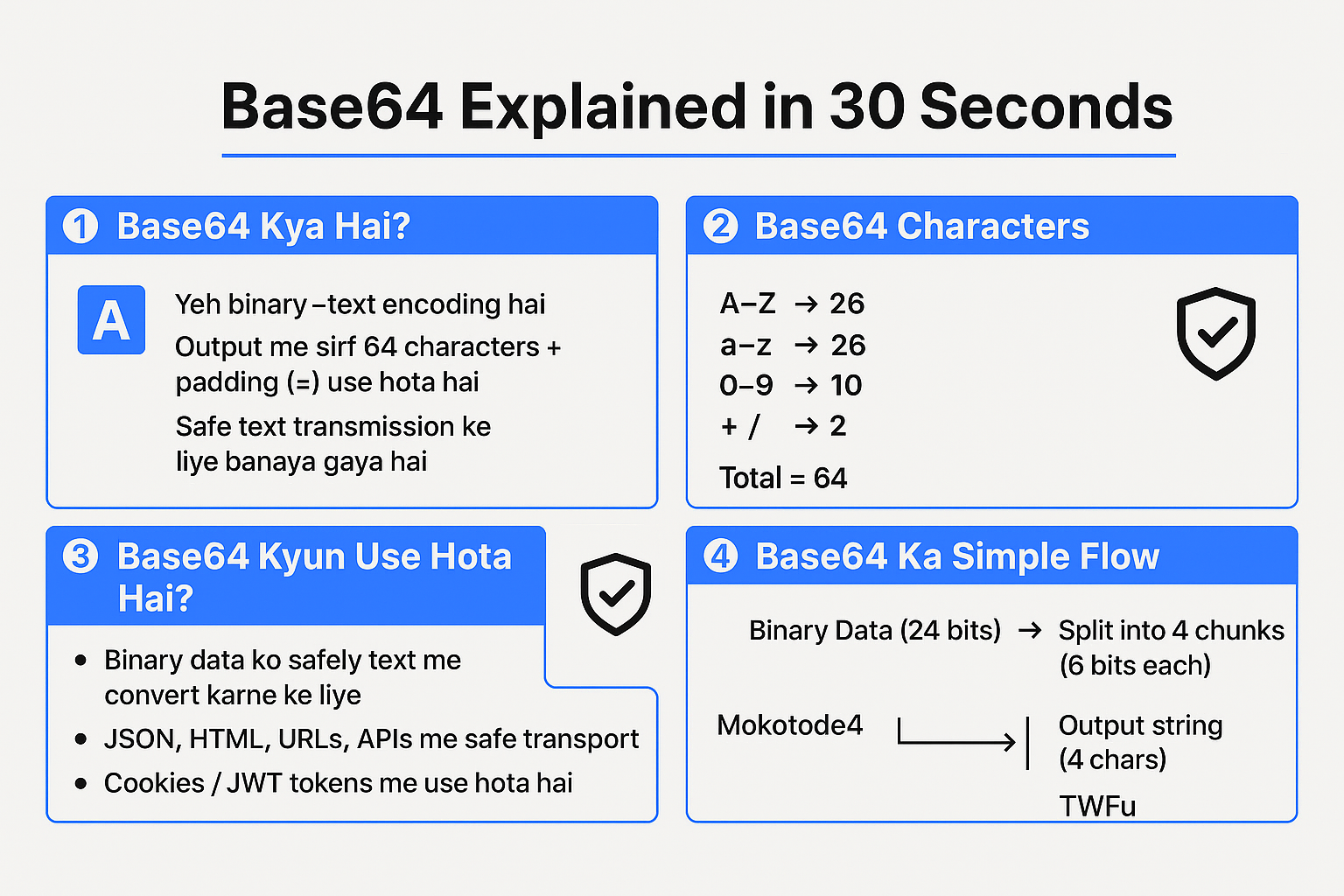
Base64 is a binary-to-text encoding scheme.
That means:
- Input: Any binary data (string, image, file, etc.)
- Output: A string made of only 64 characters + = for padding
Those 64 characters are:
- Uppercase letters: A–Z (26)
- Lowercase letters: a–z (26)
- Digits: 0–9 (10)
- Symbols: + and / (2)
Total: 26 + 26 + 10 + 2 = 64 → Base-64.
So Base64 is just a safe text representation of binary data.
2. Why Do We Need Base64?
Many protocols and formats (like URLs, headers, JSON, HTML attributes) are designed to work reliably with text characters only.
If we try to directly put raw binary data or special characters, things may break.
Base64 solves this by:
- Converting any data into a restricted, safe character set
- Making it easy to transmit over HTTP, email, JSON, URLs, etc.
3. How Base64 Works (Conceptual View)
You don’t need to do bit calculations manually in JavaScript (functions handle it), but understanding the logic helps:
- Take binary data and break it into chunks of 3 bytes (24 bits).
- Split 24 bits into 4 groups of 6 bits each.
- Each 6-bit group can represent a value from 0–63.
- Use that number to map into the Base64 character set.
If input length is not a multiple of 3:
- Padding with = is used to make the final output a multiple of 4 characters.
Example (very simplified idea):
- Input: "Man" → bytes of M, a, n
- Output: "TWFu" in Base64
4. Encoding vs Decoding
- Encoding:
Binary → Base64 text
- In browser: btoa()
- In Node.js: Buffer.from(data).toString('base64')
- In browser: btoa()
- Decoding:
Base64 text → Original binary
- In browser: atob()
- In Node.js: Buffer.from(base64, 'base64').toString('utf8')
- In browser: atob()
A base64 decoder is simply a function or tool that converts Base64 back to its original form.
2. Encoding Base64 in JavaScript
Let’s start from the basics and go deep.
1. Base64 Encoding in the Browser Using btoa()
Most modern browsers provide a built-in function:
const original = "Hello, World!";
const encoded = btoa(original);
console.log(encoded); // Output: "SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ=="
- btoa() takes a string (assumed to be Latin-1 / ASCII) and returns its Base64 representation.
But there’s a big catch: btoa() doesn’t support full Unicode strings directly.
Try this:
const text = "हेलो"; // Hindi
const encoded = btoa(text); // ⚠ This will throw an error
You’ll get:
"InvalidCharacterError: String contains an invalid character"
2. Handling Unicode Properly in the Browser
To safely encode any Unicode string, we must first convert it into UTF-8 bytes.
Option 1: Using TextEncoder (modern & recommended)
function base64EncodeUnicode(str) {
const encoder = new TextEncoder(); // UTF-8 encoder
const bytes = encoder.encode(str); // Uint8Array of bytes
let binary = "";
bytes.forEach((byte) => {
binary += String.fromCharCode(byte);
});
return btoa(binary); // Encode to Base64
}
const text = "नमस्ते दुनिया ";
const encoded = base64EncodeUnicode(text);
console.log(encoded);
What’s going on?
- TextEncoder → converts string to UTF-8 bytes.
- We build a binary string from those bytes.
- Use btoa() to convert that binary string into Base64.
Option 2: Legacy trick using encodeURIComponent (not as clean, but common)
function base64EncodeUnicodeLegacy(str) {
return btoa(
encodeURIComponent(str).replace(/%([0-9A-F]{2})/g, (match, p1) =>
String.fromCharCode("0x" + p1)
)
);
}
const text = "नमस्ते दुनिया";
const encoded = base64EncodeUnicodeLegacy(text);
console.log(encoded);
This works too, but TextEncoder is more explicit and modern.
- Base64 Encoding in Node.js Using Buffer
In Node.js, you do not have btoa() or atob() by default (unless a polyfill is used).
Instead, Node gives you the Buffer class.
const data = "Hello from Node.js";
const encoded = Buffer.from(data, "utf8").toString("base64");
console.log(encoded); // "SGVsbG8gZnJvbSBTb2RlLmpz"
Here:
- Buffer.from(data, "utf8") → creates a buffer from the string
- .toString("base64") → encodes the buffer as Base64
You can treat this as your built-in base64 encoder, and the reverse as a base64 decoder (we’ll see later).
- Encoding JSON Objects to Base64
A common use case: encode JSON payloads as Base64 for tokens, cookies, or compact transport.
Browser or Node.js (same logic, just different Base64 function):
const user = {
id: 123,
name: "Lalit",
role: "admin"
};
// Step 1: Convert to JSON string
const jsonString = JSON.stringify(user);
// Browser:
const encodedBrowser = btoa(jsonString);
// Node:
const encodedNode = Buffer.from(jsonString, "utf8").toString("base64");
console.log(encodedBrowser);
console.log(encodedNode);
To decode, you’ll parse back with JSON.parse() after using your base64 decoder.
2.5 Encoding Binary Data (Images, Files) to Base64
Base64 is often used to embed images or files as data URLs.
2.5.1 Encoding a File to Base64 in Browser
Let’s say a user uploads a file and you want its Base64:
<input type="file" id="fileInput" />
<script>
const fileInput = document.getElementById("fileInput");
fileInput.addEventListener("change", () => {
const file = fileInput.files[0];
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = () => {
const base64String = reader.result; // This is usually a data URL
console.log(base64String);
// Example: "data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg..."
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file); // Reads file and encodes as Base64 data URL
});
</script>
This gives you something like:
data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg...
If you only want the pure Base64 string (without the data:...;base64, prefix):
const base64Only = base64String.split(",")[1];
2.5.2 Encoding ArrayBuffer or Uint8Array
If you already have an ArrayBuffer (e.g., from a fetch of a binary file):
function arrayBufferToBase64(buffer) {
let binary = "";
const bytes = new Uint8Array(buffer);
bytes.forEach((b) => (binary += String.fromCharCode(b)));
return btoa(binary);
}
// Example usage:
fetch("image.png")
.then((res) => res.arrayBuffer())
.then((buffer) => {
const base64 = arrayBufferToBase64(buffer);
console.log(base64);
});
- Decoding Base64 in JavaScript (Base64 Decoder)
Now let’s focus on the base64 decoder side - taking Base64 and getting back original data.
1. Decoding Base64 in the Browser Using atob()
Basic usage:
const encoded = "SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==";
const decoded = atob(encoded);
console.log(decoded); // "Hello, World!"
Again, atob() expects and returns Latin-1 / ASCII text.
If your original text was Unicode, you need an extra step.
2. Decoding Unicode Strings from Base64 (Browser)
Corresponding to our encoder, we will create a Unicode-safe base64 decoder.
Using TextDecoder:
function base64DecodeUnicode(base64Str) {
const binary = atob(base64Str); // Base64 → binary string
const len = binary.length;
const bytes = new Uint8Array(len);
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
bytes[i] = binary.charCodeAt(i);
}
const decoder = new TextDecoder(); // Default: UTF-8
return decoder.decode(bytes); // Bytes → original string
}
const text = "नमस्ते दुनिया";
const encoded = base64EncodeUnicode(text); // From previous section
const decoded = base64DecodeUnicode(encoded);
console.log(decoded); // "नमस्ते दुनिया"
If you used the legacy encodeURIComponent trick for encoding, you can decode similarly:
function base64DecodeUnicodeLegacy(base64Str) {
return decodeURIComponent(
atob(base64Str)
.split("")
.map((c) => "%" + c.charCodeAt(0).toString(16).padStart(2, "0"))
.join("")
);
}
- Base64 Decoder in Node.js Using Buffer
In Node.js, Buffer again acts as the encoder/decoder pair.
const encoded = "SGVsbG8gZnJvbSBTb2RlLmpz";
const decoded = Buffer.from(encoded, "base64").toString("utf8");
console.log(decoded); // "Hello from Node.js"
- Buffer.from(encoded, "base64") → interprets the input as Base64
- .toString("utf8") → converts bytes to a UTF-8 string
This is your base64 decoder implementation in Node.js.
You can wrap it in a helper:
function base64DecodeNode(base64Str) {
return Buffer.from(base64Str, "base64").toString("utf8");
}
- Decoding Base64 JSON Payloads
If you encoded JSON earlier, decoding is straightforward:
// Browser example
const encoded = btoa(JSON.stringify({ id: 123, name: "Lalit" }));
const jsonString = atob(encoded);
const obj = JSON.parse(jsonString);
console.log(obj.id); // 123
console.log(obj.name); // "Lalit"
Node.js:
const encoded = Buffer.from(
JSON.stringify({ id: 123, name: "Lalit" }),
"utf8"
).toString("base64");
const decodedJson = Buffer.from(encoded, "base64").toString("utf8");
const obj = JSON.parse(decodedJson);
console.log(obj);
- Decoding Base64 Images in the Browser
Assume we have a Base64 data URL and we want to show it in an <img> tag:
const base64DataUrl = "data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg...";
const img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = base64DataUrl;
document.body.appendChild(img);
If you have only the raw Base64 string, you can prefix it:
const base64 = "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg..."; // pure Base64 (no prefix)
const img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = `data:image/png;base64,${base64}`;
document.body.appendChild(img);
Convert Base64 to Blob or File
function base64ToBlob(base64, contentType = "", sliceSize = 512) {
const byteCharacters = atob(base64);
const byteArrays = [];
for (let offset = 0; offset < byteCharacters.length; offset += sliceSize) {
const slice = byteCharacters.slice(offset, offset + sliceSize);
const byteNumbers = new Array(slice.length);
for (let i = 0; i < slice.length; i++) {
byteNumbers[i] = slice.charCodeAt(i);
}
const byteArray = new Uint8Array(byteNumbers);
byteArrays.push(byteArray);
}
return new Blob(byteArrays, { type: contentType });
}
Usage:
const base64 = "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg..."; // image bytes
const blob = base64ToBlob(base64, "image/png");
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
const img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = url;
document.body.appendChild(img);
- What Are the Benefits of Base64?
Base64 is not magic, but it has some serious practical advantages.
1. Safe Transmission of Binary Data Over Text-Only Channels
Some channels (like legacy email, certain APIs, or logs) only handle printable text reliably.
Base64 ensures:
- No control characters
- No issues with newlines, quotes, or special symbols
2. Easy Embedding in HTML, CSS, and JSON
Common use cases:
- Embedding images as data URLs in HTML or CSS
- Embedding configuration or payloads in JSON
- Storing compact tokens or config in environment variables
Example: CSS background image with Base64:
.element {
background-image: url("data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg...");
}
3. Simpler Debugging and Copy–Paste
Compared to raw binary, Base64:
- Can be copied/pasted in editors, terminals, logs
- Can be quickly checked using any base64 decoder tool
4. Standard and Widely Supported
Base64 is standardized in multiple RFCs and supported across:
- Browsers (btoa, atob)
- Node.js (Buffer)
- Almost all languages (Java, Python, Go, PHP, etc.)
This makes it a good interoperability layer.
- What Are the Limitations of Base64?
Base64 is not perfect. You should know its drawbacks.
1 Increased Size (≈33% Overhead)
Base64 makes data about 33% larger.
- 3 bytes → 4 Base64 characters
- So the storage and bandwidth usage increase
For example:
- Binary image: 1 MB
- Base64 image: ~1.33 MB
For large files, this can be significant.
2. Not Encryption (No Real Security)
Very important point:
Base64 is not encryption. It’s just encoding.
Anyone can run a base64 decoder (online or via code) and get the original data back easily.
So:
- Do not use Base64 as a security or obfuscation mechanism.
- For real security, use proper crypto algorithms (AES, RSA, etc.) and TLS.
3. Performance Impact for Large Data
- Encoding/decoding large files (like videos or big images) in JavaScript (especially in browser) can be slow and memory-heavy.
- For such cases, it’s better to keep data as binary streams instead of converting to Base64.
4. URL and Filename Issues
Base64 output may contain characters like +, /, and =.
- In URLs, + might be interpreted as space, / as path separator, etc.
- We need URL-safe Base64 variants or encoding.
We’ll touch on URL-safe Base64 below in best practices.
- How to Encode Data with Base64 in JavaScript (Step by Step)
Let’s summarize practical workflows for different environments and data types.
1. Strings in Browser
ASCII-only string:
const message = "Simple text";
const base64 = btoa(message);
Unicode string (safe method):
const message = "नमस्ते दुनिया";
const base64 = base64EncodeUnicode(message); // from earlier function
2. Strings in Node.js
const message = "नमस्ते दुनिया";
const base64 = Buffer.from(message, "utf8").toString("base64");
console.log(base64);
3. JSON Payloads
Encode:
const payload = { id: 1, email: "[email protected]" };
const jsonStr = JSON.stringify(payload);
// Browser
const base64 = btoa(jsonStr);
// Node
// const base64 = Buffer.from(jsonStr, "utf8").toString("base64");
Decode:
// Browser
const decodedJsonStr = atob(base64);
const data = JSON.parse(decodedJsonStr);
// Node
// const decodedJsonStr = Buffer.from(base64, "base64").toString("utf8");
// const data = JSON.parse(decodedJsonStr);
4. Encoding Data for URL (URL-Safe Base64)
Sometimes you want Base64 inside URLs. You can convert to URL-safe by replacing characters:
function toUrlSafeBase64(base64Str) {
return base64Str.replace(/\+/g, "-").replace(/\//g, "_").replace(/=+$/, "");
}
function fromUrlSafeBase64(urlSafeStr) {
let base64 = urlSafeStr.replace(/-/g, "+").replace(/_/g, "/");
// Add padding back if needed
while (base64.length % 4 !== 0) {
base64 += "=";
}
return base64;
}
Use case:
const payload = { userId: 123 };
const json = JSON.stringify(payload);
const base64 = btoa(json);
const urlSafe = toUrlSafeBase64(base64);
const url = `https://example.com/reset?token=${encodeURIComponent(urlSafe)}`;
Later on server, reverse the process using your base64 decoder.
- Pitfalls and Best Practices
Now let’s talk about common mistakes and how to avoid them.
1. Pitfall: Assuming Base64 Is Encryption
Mistake:
Storing sensitive data as Base64 and thinking it's safe.
Fix / Best Practice:
- Understand Base64 is reversible with any base64 decoder.
- Use encryption (like AES) if you need security, then optionally Base64-encode the ciphertext for transport.
- Pitfall: Unicode Handling with btoa / atob
Mistake:
Passing arbitrary Unicode text directly to btoa() and reading from atob() directly.
Fix / Best Practice:
- Always convert Unicode strings to bytes (TextEncoder) before btoa.
- After decoding with atob, convert the binary string back to text using TextDecoder.
- Pitfall: Using Base64 for Very Large Files in Browser
Mistake:
Converting large images/videos entirely into Base64 in the browser, causing memory and performance issues.
Fix / Best Practice:
- Prefer streaming or direct binary transfer where possible.
- Use URLs (e.g., object URLs) instead of data URLs for large assets.
- Pitfall: Forgetting About Size Overhead
Mistake:
Embedding lots of Base64 images in HTML or CSS and wondering why page size is huge.
Fix / Best Practice:
- Use Base64 only when advantageous (e.g., small inline icons, avoiding extra HTTP requests).
- For big images, serve them as normal image files via URLs/CDN.
- Pitfall: Ignoring URL-Safety
Mistake:
Sending raw Base64 strings in URLs and facing issues due to +, /, or =.
Fix / Best Practice:
- Use URL-safe Base64 variants (replace +// and trim =).
- Or always wrap tokens with encodeURIComponent() / decodeURIComponent() when using URLs.
- Pitfall: Double Encoding
Mistake:
Encoding the same data multiple times by mistake:
original → Base64 → again Base64 → broken
Fix / Best Practice:
- Keep track of whether your data is already encoded.
- Have clear naming, like:
- data
- dataBase64
- dataDecoded
- data
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Let’s close with a FAQ section focused around Base64 and base64 decoder concepts in JavaScript.
Q1. What is a base64 decoder in JavaScript?
A base64 decoder in JavaScript is any function that takes a Base64-encoded string and returns the original data (usually text or bytes).
- In browsers: atob(base64String)
- In Node.js: Buffer.from(base64String, "base64")
Example (browser):
const decoded = atob("SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==");
Example (Node):
const decoded = Buffer.from("SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ==", "base64").toString("utf8");
Q2. Is Base64 encoding the same as encryption?
No.
Base64 is not encryption, it is just an encoding.
- Purpose: make binary data text-safe
- Anyone can decode it with a base64 decoder
- It does not protect confidentiality
For security, you must use encryption algorithms.
Q3. Why does Base64 increase string size?
Because Base64 represents 3 bytes of binary data using 4 characters (each from 64 possibilities).
- 3 bytes (24 bits) → 4 x 6 bits = 24 bits
- So output grows by about 33%.
Q4. When should I use Base64?
Use Base64 when:
- You need to embed binary data in text-based structures (JSON, HTML, XML).
- You want to avoid issues with binary or special characters over protocols that expect text.
- You want to quickly copy/paste or log data safely.
Avoid it for:
- Very large files where overhead and performance matter.
- Security use-cases (it’s not encryption).
Q5. What is the difference between btoa/atob and Buffer?
- btoa / atob:
- Available in browsers
- Work on strings assuming ASCII/Latin-1
- Need extra steps for Unicode
- Available in browsers
- Buffer:
- Node.js feature
- Works directly with bytes
- Can encode/decode using "base64" and "utf8" easily
- Node.js feature
// Browser
const base64 = btoa("Hello");
// Node
const base64Node = Buffer.from("Hello", "utf8").toString("base64");
Q6. How do I decode a Base64 string that represents JSON?
- Decode Base64 to string using a base64 decoder.
- Parse JSON.
Browser:
const encoded = btoa(JSON.stringify({ id: 1 }));
const decodedJsonStr = atob(encoded);
const obj = JSON.parse(decodedJsonStr);
Node:
const encoded = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify({ id: 1 }), "utf8").toString("base64");
const decodedJsonStr = Buffer.from(encoded, "base64").toString("utf8");
const obj = JSON.parse(decodedJsonStr);
Q7. How do I decode a Base64 image and show it in the browser?
If you have a Base64 string (without prefix):
const base64 = "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUg...";
const img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = `data:image/png;base64,${base64}`;
document.body.appendChild(img);
If you want a file-like object:
- Use base64ToBlob (shown earlier), then create an object URL.
Q8. What is URL-safe Base64?
URL-safe Base64 replaces characters that can cause issues in URLs:
- + → -
- / → _
- Optional: remove trailing =
Many APIs and JWTs use URL-safe Base64.
You can convert using helper functions like toUrlSafeBase64 and fromUrlSafeBase64 from earlier sections.
Q9. Can Base64 be used as a checksum or validation?
No.
Base64 does not verify integrity. It does not detect tampering.
For validation:
- Use checksums (MD5, SHA-256)
- Or signed tokens (HMAC, JWT with signature)
Q10. Is it safe to use online base64 decoder tools?
For non-sensitive data, yes, it’s fine.
For sensitive data (passwords, tokens, private keys):
- Avoid pasting into online tools.
- Use local tools or write your own base64 decoder in JavaScript/Node instead.
Conclusion
Base64 encoding and decoding play an essential role in modern web and application development. Whether you are working with APIs, transmitting binary data, handling JSON payloads, or embedding images directly into HTML/CSS, Base64 provides a reliable and universally supported way to convert raw data into a safe, text-based format.
In this article, we explored:
- What Base64 encoding and decoding actually are
- How the Base64 algorithm works behind the scenes
- How to encode and decode strings in JavaScript using btoa(), atob(), and Buffer
- How to properly handle Unicode text, JSON objects, images, files, and binary data
- Key benefits and limitations of using Base64
- Real examples and best practices developers must follow
- Common mistakes to avoid while implementing Base64 in JavaScript
One important takeaway is that Base64 is not encryption. It does not provide security or protect sensitive information. It simply converts binary data into a text format that can be safely stored, transferred, or embedded. For security, encryption algorithms must be used - not Base64.
If you apply the techniques and knowledge shared in this article, you will be able to confidently implement Base64 encoding and decoding in any JavaScript environment, whether in the browser, Node.js, or hybrid applications.
Base64 is a small concept, but it has a massive impact on how data flows across the web. Understanding it deeply makes you a better, more reliable, and more efficient developer.
Also read:-