An Application Programming Interface (API) provides a format for software programs to communicate with each other through defined interfaces or "rules." By creating a platform for programs, APIs enable developers to share data and functionality securely and efficiently, while lowering development time through automation and code reuse of small pieces of already written code to make larger applications more adaptable.
An API is involved when you book a flight, pay with UPI, check the weather on your phone, or log into an app with Google or Facebook. It’s the invisible layer that allows applications, platforms, and devices to “talk” to each other. APIs are now the core of modern software design. They let systems talk to each other easily and safely, without showing the complicated details inside.
This guide covers everything you need to know about APIs. It begins with the basics. Then, it gives real-world examples, types of APIs, how they work, and why developers and businesses rely on them today. This blog is for everyone. If you're a curious beginner, a new developer, or a business leader, you'll find clear and useful insights about APIs here.
What is an API?
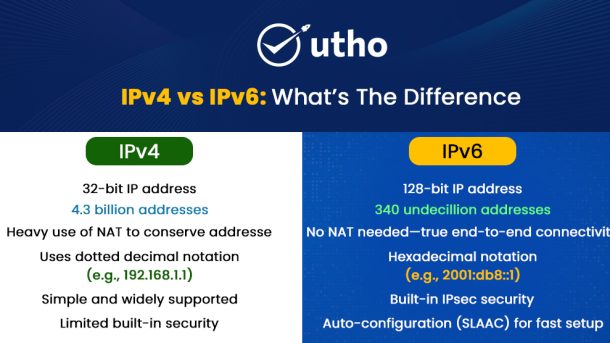
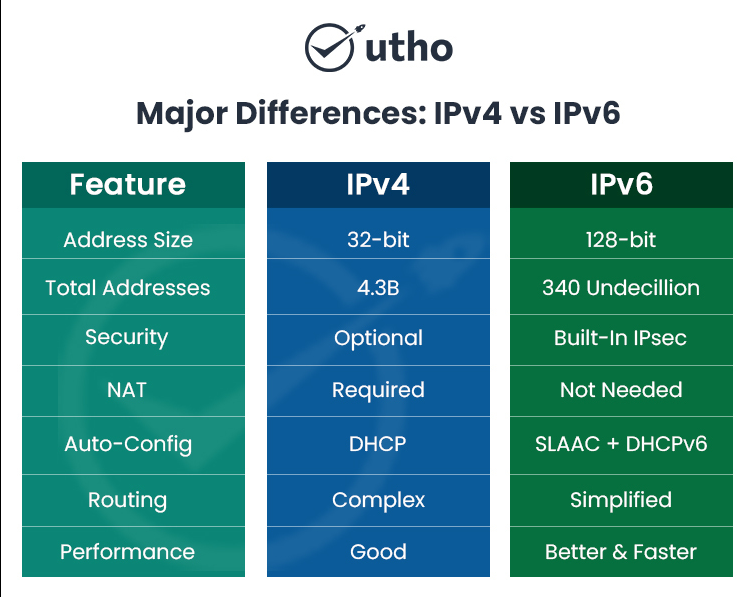
API stands for Application Programming Interface. An API is the underlying technology that allows modern software applications to operate together. It does this by allowing software applications to work with one another and exchange information.
- An API allows software applications, platforms, and services to easily work together.
- APIs provide many of the everyday conveniences that people use, such as checking the weather, receiving payment notifications, and shopping online.
API Full Form
API stands for Application Programming Interface. An API allows different applications to exchange information seamlessly without needing to know how the other programs are implemented internally.
Why do we need APIs?
APIs are needed to enable different software systems to communicate, share data, and work together efficiently and securely.
Key reasons we need APIs:
- Communication & Integration: APIs allow software components to communicate with one another by providing a set of guidelines. A weather app uses APIs to access data provided by a weather bureau, while an e-commerce website updates its product inventory through API access to a back-end database.
- Faster Development: Rather than creating from scratch, developers can utilize simplified code libraries that contain semi-complete programming functions by providing pre-packaged application programming interfaces (APIs).
- Data Access: APIs allow standardized, secure, and consistent access to information across multiple locations. This means all of this information can be evaluated together and provides the opportunity to create a significant amount of analytical and data-driven information.
- Security: The use of APIs to mediate between an application and the underlying system, while only providing access to essential functions, enhances security by providing an additional layer of indirection.
- Innovation: Connection via APIs allows businesses to create new features quickly and create completely new applications, enabling rapid digital transformation and growth of business models.
How Does an API Actually Work?
An application programming interface (API) allows two independent software applications to communicate through a set of defined rules and standards for exchanging information. It serves to relay requests made by one program, a client, to another program, a server, and return a result.
The API Request-Response Cycle: How Communication Happens
The API communicates through a request-response cycle, which happens over the Internet with the use of the HTTP protocol. This process consists of four main steps:
- A request is initiated: A user action causes the app to make an API call by sending an HTTP request to a defined endpoint. The HTTP request will contain the HTTP method, the authorization and data type headers, and possibly a body that includes the information to be sent.
- The server processes the request: The API server receives a request from a client, verifies its identity (authentication), and processes the request per the API server's internal workings. This typically requires querying an internal database or interacting with other systems.
- A Response Is Generated: The reply is returned from the server based on the request. This reply will have a response status code and response headers, as well as a reply body that contains the data requested, typically in either JSON or XML format.
- The Client Receives the Response: The original client application receives a reply from the API. The client will next process this information and present it to the user (e.g., correcting the way that the client presents the current weather).
API Architecture Workflow
API architecture is a detailed design of an API. It outlines how an application will function, what types of systems it will interact with, what types of information will be exchanged between systems, and how those exchanges will be protected. API architecture provides security, performance, scalability and ease of use for the API's users.
Here are some common API architecture styles:
REST (Representational State Transfer)
REST APIs are a widely accepted, adaptable API structure based on the stateless process of creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting a resource utilizing the HTTP protocol to access it. RESTful APIs utilize unique identifiers, URIs, as a means of accessing resources and typically employ either XML or JSON file formats to transfer data.
GraphQL
GraphQL is an innovative way to request specific information with just one request. It allows users to access exactly what they want from one source by giving them complete control over their requests. This is accomplished through a single endpoint and flexible methods of requesting data.
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
The older, more rigid protocol uses XML for message formatting and a strict contract defined by a WSDL file. It is ideal for enterprise environments that place a premium on high levels of security and consistency and transactional integrity, such as bank systems.
gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call)
The Remote Procedure Call framework consists of RPCs and Protocol Buffers, allowing the creation of a high-performing framework. Because it supports the use of HTTP/2 for efficient data transfer and supports data streaming, the framework is ideal for applications with low-latency requirements, as well as internal communication between microservices.
WebSocket
The WebSocket protocol allows a persistent and full-duplex (two-way) communication channel between a client and a server over one connection. Thus, it is perfect for real-time applications (online games, chat applications, and live dashboards) that require instant transfer of data between the client and server.
Key Components of an API Request
An API request to a web service comprises five key components:
Endpoint URL
An API endpoint provides access to specific resources or actions on a web server, so an API request has a defined address that highlights or provides access to these resources and actions. An API endpoint comprises a base URL (e.g., https://api.example.com) combined with a specific path for the resource requested (e.g., /users/123).
HTTP Method
This element indicates what the client would like to do with the given resource at the URL in question. There are several types of methods; however, here are some common examples.
- GET: Retrieve data.
- POST: Create a new resource or submit data.
- PUT: Update an existing resource (replaces the entire resource).
- PATCH: Partially update an existing resource.
- DELETE: Remove a resource.
Headers
The request also contains additional metadata in the form of key:value pairs. This extra metadata includes things like the authentication credentials (e.g., Authorization: Bearer <token>), the expected type of data (e.g., Content-Type: application/json, Accept: application/json), and caching directives.
Parameters
These are the variables passed to the endpoint to offer specific instructions or refine the request. There are two parameters:
- Query Parameters
- Path Parameters
Request Body (Payload)
The optional part is where the actual information that will be sent to the server is located and is solely used when making a POST, PUT, or PATCH request. It includes a created or changed object in an existing resource. Most of the content will be encapsulated in either a JSON or XML structure.
Types of APIs
APIs are categorized based on their accessibility, purpose, and usage. Here are the major types of APIs, such as Web, Local, Program, Internal, Partner, and Open (Public APIs).
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Web APIs | Accessed over the internet using HTTP/HTTPS to enable communication between web-based systems. | Stripe API, Google Maps API |
| Local APIs | Operate within a local system or operating environment to access system-level functions. | POSIX API, macOS Cocoa API |
| Program APIs | Enable applications to communicate remotely using structured procedure calls. | gRPC, Apache Thrift |
| Internal APIs | Designed for private use within an organization to support internal services. | Internal HR service APIs |
| Partner APIs | Shared securely with selected partners for business integration. | PayPal Partner API |
| Open (Public) APIs | Publicly available APIs that developers can use to build third-party applications. | Spotify API, OpenWeather API |
Real-World Examples of APIs
Real-world examples of APIs include Payment Processing Systems, Social Media Integration, Maps and Location Services, and Weather applications.
- Payment Processing System: Stripe, PayPal, and similar services use application programming interfaces (APIs) to let eCommerce sites process payments in a secure fashion without needing to store customer-sensitive credit card information.
- Social Media Integration: Numerous websites give you the option to log in with your Google, Facebook, or Apple account. This is accomplished using authentication APIs, which confirm your identity to the website by working with the third-party services and supplying the appropriate identifying information from those services to the website.
- Maps and Location Services: Uber and Lyft will often integrate the Google Maps API to allow users to view Maps and get directions and to allow a user to track where the vehicle is and when they might arrive.
- Weather Applications: If you use the Weather application on your phone or look up the weather via a rich snippet in Google Search, this application is not producing the forecast for you. Rather, this application will utilize Weather APIs like OpenWeatherMap to retrieve current weather data from meteorological services via an API.
Tools for API Development and Testing
There are several tools commonly used in different stages of the API development cycle to assist with design, functional testing, performance testing, and security.
- Postman: A comprehensive API tool that provides an easy-to-use graphical user interface for designing, testing, documenting, and monitoring APIs.
- SoapUI/ReadyAPI: SoapUI is an open-source, free tool for performing functional, security, and load testing of REST/SOAP APIs.
- Apache JMeter: An open-source and cross-platform performance and load test tool that is ideally used to simulate very busy traffic and assess API performance under stress.
- Insomnia: A lightweight and easy-to-use interface for use with multiple APIs such as REST, SOAP, and GraphQL (using test suites, etc.) that makes it easy to build and test with minimal code.
- Swagger/OpenAPI: It is a full suite of tools created to manage the entire API lifecycle. They are perhaps known best as tools for designing and documenting APIs using the OpenAPI specification by generating interactive documentation and code for applications that can run on the client or server side of the API.
Building a Simple REST API in Node.js with Express
To truly understand how APIs work, nothing beats building one yourself. Let’s walk through a basic example using Node.js and the Express framework — two popular tools for server-side JavaScript development.
What We’re Building
We’ll create a small REST API with a single endpoint that responds with a friendly JSON message. This is often the first step when learning how to work with APIs.
Setting Up the Project
First, make sure you have Node.js and npm installed on your system. Then, initialize your project:
npm init -y
npm install express
Writing the API Code
Create a file named index.js and add the following code:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
// Define a simple GET endpoint
app.get('/api/hello', (req, res) => {
res.json({ message: 'Hello, world!' });
});
// Start the server
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
Breaking It Down
- express: This is the web framework we’re using to build the API.
- app.get('/api/hello'): We define a route (endpoint) that listens for GET requests on /api/hello.
- res.json({ message: 'Hello, world!' }): This sends a JSON response back to the client.
app.listen(PORT): This starts the server and listens on the specified port (3000 in this case).
Testing the API
Once you run the file using:
node index.js
Open your browser or an API testing tool like Postman and visit:
http://localhost:3000/api/hello
You should see the response:
{
"message": "Hello, world!"
}
Why This Matters
This simple example teaches you the core of API building:
- Creating routes
- Sending JSON responses
- Running a server
- Understanding the HTTP request-response cycle
Once you grasp this, you're ready to move on to more advanced topics like authentication, connecting to databases, and deploying your API to the cloud.
Common API Status Codes
When working with APIs, it's important to understand HTTP status codes. These codes are returned by the server to indicate the result of your request:
- 200 OK – The request was successful, and the response contains the requested data.
- 201 Created – The request was successful and a new resource was created (typically used with POST requests).
- 400 Bad Request – The request is invalid, often due to malformed syntax or missing parameters.
- 401 Unauthorized – The client is not authenticated. API access usually requires a valid token or key.
- 404 Not Found – The requested resource could not be found on the server.
- 500 Internal Server Error – Something went wrong on the server while processing the request.
Understanding these codes helps you debug faster and improve error handling in your applications.
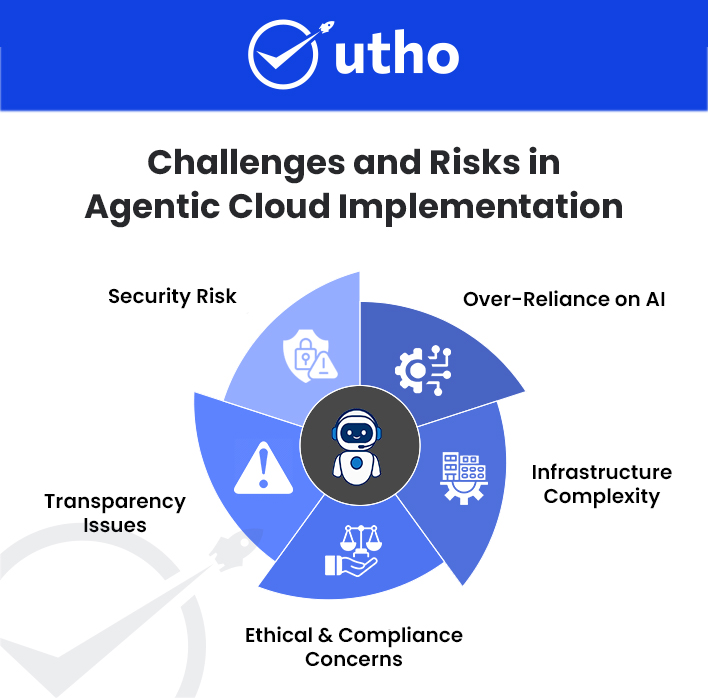
Challenges in Working with APIs
Developers and organizations face many challenges when using APIs, including technical and operational management challenges.
Poor and Outdated Documentation
One of the most common frustrations for developers is that the API will have incomplete, inaccurate, or otherwise difficult documentation. Developers often find it challenging to navigate through endpoint information, what parameters are required to communicate with the API, how to authenticate, and how to handle errors when using the API.
Security Risks
APIs provide access to an application’s endpoints and will usually contain sensitive information, which makes APIs a prime target for cyberattacks. A common vulnerability when working with an API includes broken authentication, insufficient authorization, exposure of data, and injection attacks.
Performance & Scalability
As the number of requests to your API increases, it becomes increasingly important for the API to continue delivering fast responses. Performance bottlenecks like high latency caused by ineffective database querying, unnecessarily large data payloads, or poor coding practices will degrade user experience and increase the cost of maintaining your infrastructure.
Error Handling & Debugging
Finding the source of API request failure can often take a while if you received an error message that isn’t up to any specific standard and doesn’t say much. To correctly debug, one must have a good understanding of the API and the other system they're integrating with.
Complexity and Integration
Developers face difficulties in developing and managing various API integrations because of their complexity and time-consuming nature. Developers are confronted with a large number of different data types (XML or JSON), communication protocols, and logical structures that vary from one system to another.
The Future of APIs
API development and architecture have changed significantly over time, and as a result, API development is focused on supporting large-scale system demands. This includes the use of AI in an API, as well as machine learning and intelligence as part of the API. Additionally, serverless APIs avoid managing server-based computing through the use of cloud functions. technology. Event-driven APIs include real-time system events. Finally, advanced API gateways ensure that APIs are secure, optimally performing, manageable for traffic control, and able to be integrated across wide geographical areas.
Utho API: The Power to Program Your Cloud
To be efficient, companies must embrace automation within their business models. Automated management of cloud infrastructures utilizes Cloud APIs from third-party services (e.g., Amazon Web Services) to interact with cloud providers and perform tasks programmatically. For example, using Utho's API, developers can manipulate nearly every aspect of a cloud provider's services (e.g., deploying a VM, attaching storage, creating a VPC)—all via clean, clear code.
Utho was purposefully built using contemporary development techniques for ease of use via multiple programming languages, including Python, Node.js, Go, etc. By making a few simple calls to the API, you can perform a variety of actions, including launching new instances, attaching storage volumes, configuring a virtual private cloud (VPC), creating a snapshot of your instance at any time, creating security groups, and monitoring usage. You can accomplish all of this without ever accessing the cloud provider's management console.
Conclusion
APIs serve as an integral aspect of contemporary software development, facilitating a seamless transfer of information and function between applications and services. APIs increase integration, scalability, and efficiency, which provides developers with tools to create flexible, connected digital solutions across platforms and technologies today and into the future.