How To Install Java on Fedora server

How to install Java on Fedora server
In this tutorial, we will learn how to install Java on Fedora server. Linux comes in many different flavours, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, Fedora, and Rocky Linux. Java is a popular programming language and software platform that lets users run many different programmes that are meant to run on a server.
Prerequisites
- Any super user( root ) or any normal user with SUDO privileges
- dnf repository configured server
1 – Installing Java- OpenJDK
Users can choose from Standard Edition (SE), Enterprise Edition (EE), and Micro Edition, which are all different versions of the Java Platform (ME). This whole book is all about Java SE (Java Platform, Standard Edition). Java software that is both open source and free is usually made to work with Java SE.
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and the Java Development Kit (JDK) are both Java SE packages that can be downloaded and installed on a computer (JDK). The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is a version of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that lets you run already-made applets and Java programmes. The Java Development Kit (JDK) comes with the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and other software needed to design, build, and develop Java programmes and applets.
OpenJDK and Oracle Java are two more good choices for running Java programmes. OpenJDK, which is the reference version of Java, is completely open source. On the other hand, Oracle Java has some code that only Oracle can access and that no one else can. But most of the code for both implementations is the same. Either Java implementation should be able to run the vast majority of Java programmes without problems, but you should choose the implementation that your software needs.
Java can be installed in a number of different versions and releases, but most users only need to do a single installation. So, it's important to make sure you only install the version of Java that your application needs to create or run (s).
Using the dnf package manager, you can use the command dnf install java to install the OpenJDK.
# dnf install java
If you try to install Java without choosing a version, the OpenJDK JRE version that is the most popular stable version will be used. a From this output, you can see that the version of Java that is being used right now is 1.8.0-openjdk.
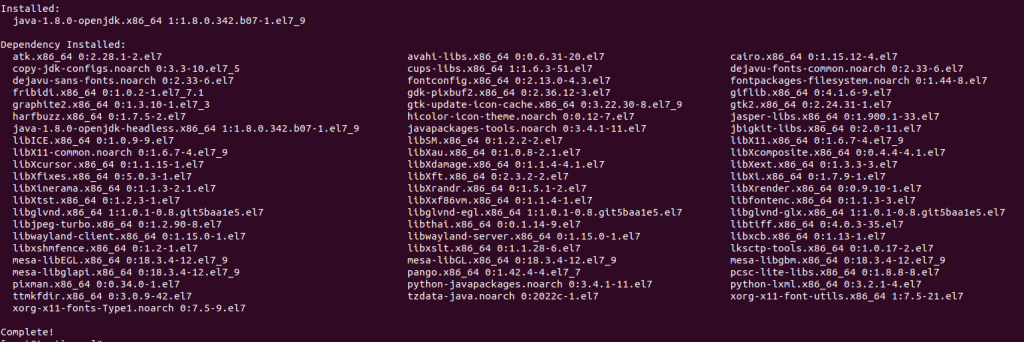
Installed java on Fedora server
You should now have a properly working Java installation. To be sure, you can use the command java -version: to find out which version of Java is installed on your computer.
java -version
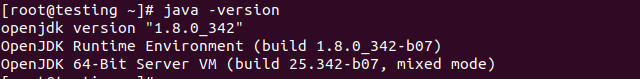
Current version of Java
To get the full OpenJDK JDK, you need to install the package with the name "-devel" added to it. This is a common way to make development packages for other programming environments, and Java does the same thing.
dnf install java-devel
2 - Install Other OpenJDK Releases
OpenJDK has changed how it numbers its versions so that they are more in line with Oracle Java releases. Like with 1.8.0, you can install a newer version of OpenJDK by putting the version number in the package name. For example, to install OpenJDK 17, type dnf install java-17-openjdk:
# dnf install java-11-openjdk-devel
3 - Setting Your Default Java Version
If you have more than one version of Java installed, you should probably make one of them the default version (i.e. the one that will run when a user runs the java command). Also, some applications need certain environment variables to be set in order to figure out which version of Java should be used.
To change the default Java version, you need to use the alternatives command, which uses symbolic links to control the default commands. Use the alternatives –config java: command to see a list of the different versions of Java that alternatives can work with.
alternatives --config java
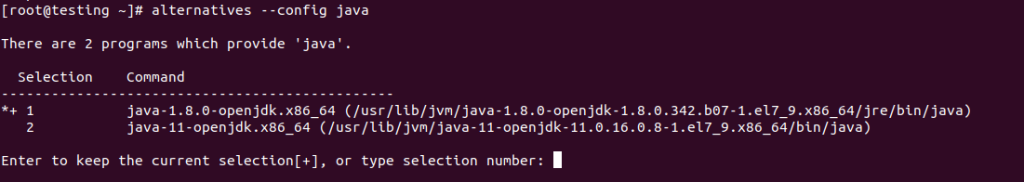
Alternatives of java version
Enter the number that corresponds to the option to choose the Java executable that will be used by default. It will change the symbolic links on your computer so that the java command will point to the right set of libraries. You can run this command as many times as you want, and each time java -version should show a different value:
java -version

latest version of Java
So this is how you will learn how to install Java on Fedora server