How to Troubleshoot with nmap in centos

Introduction
In this article, you will learn how to Troubleshoot with nmap in centos.
Nmap, which stands for "Network Mapper," is a network scanner that was developed by Gordon Lyon (also known by his pseudonym Fyodor Vaskovich). Sending out packets and evaluating the responses received from those packets is how Nmap finds hosts and services on a computer network.
Nmap is a tool that may be used to investigate computer networks and offers a variety of functions, such as host discovery and the detection of services and operating systems. Scripts can be used to extend the capabilities of these features so that they can perform more sophisticated vulnerability detection, service discovery, and other detections. During a scan, Nmap is able to adjust itself to different network conditions, such as latency and congestion.
If you read the article that has been provided for you here, you will gain more knowledge about the topics that have been discussed. How to Determine the Specifics of the Existing Issues Employing the Nmap Tool when Running on CentOS It is highly recommended that nmap be used whenever there is a requirement to determine whether or not a server is online and able to take connections. This is because nmap is an excellent tool. This decision needs to be made anytime there is a need for it. The nmap tool should be used whenever there is a need to discover whether or not a server is online and able to accept connections. This can be done when there is a need to determine whether or not a server is online. This approach to diagnosing issues with port connectivity involves use of the nmap software, which can be obtained by downloading it from the following location: Nmap is a powerful port scanning application that, once it has scanned the ports on a server, gives you information on the state of those ports as well as the server that they are located on.
nmap your server's IP address from another machine. These control toggles can in helpful:
-Pn : Treat all hosts as online and skip host discovery.
-p : List of ports to scan.
--reason : Display the reason a port is in a particular state.
Example: To scan ports 22, 53, 80, and 443 on your server IP
# nmap -Pn -p 22,53,80,443 --reason server_IP
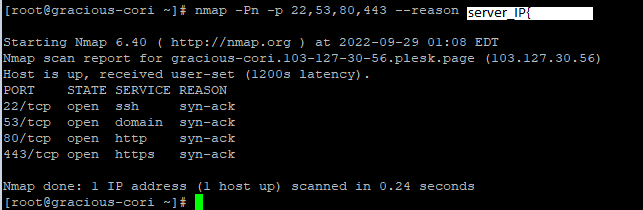
Finished scanning 1 IP address on 1 active host in 0.24 seconds with nmap.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have tested how to Troubleshoot with nmap in centos.
Also read: How To Install MariaDB 10.7 on CentOS 7
Thank You 🙂