How to use MTR command in Linux

Introduction
In this article, you will learn how to use MTR command in Linux.
My Traceroute, also known as MTR, is a tool that evaluates the state of a network connection through the use of the traceroute and ping commands.
My traceroute is a computer programme that was initially known as Matt's traceroute. It is a network diagnostic utility that combines the capabilities of the traceroute and ping computer programmes into a single application.
MTR examines routers along the route path by putting a cap on the number of hops that individual packets are allowed to take and then listening for responses about when those packets expire.
Install MTR on Linux
With the following command, you will install MTR on different operating systems.
MTR on Debian/Ubuntu
# apt-get install mtr
MTR on Fedora/CentOS
# yum install mtr
MTR on Arch/Manjaro
# pacman -S mtr
MTR on BSD
# pkg install mtr
Use of MTR
Installing MTR on your web server and running it against your local machine will help you gain a deeper comprehension of the performance problems that are affecting your network.
MTR can be used to perform real-time scans as well as scans in a summary format.
Execute mtr with a domain, server IP, or server hostname, and you will be able to view real-time performance statistics.
# mtr domain.com
# mtr Server\_IP
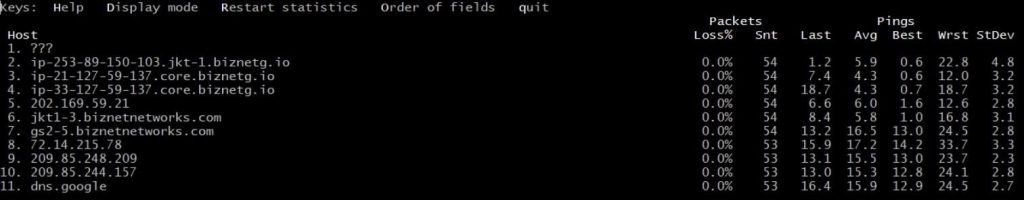
During the scan, you will have the following options that are available to you:
- Help – Display open command options for the current MTR testing
- Display mode – Change how data on packets and pings are shown
- Restart statistics – Start the test over again
- Order of fields – Change the order of the columns that are open (press Enter to leave)
- quit – Stop MTR
You can always copy the results. We suggest that you wait until you have sent at least 50 packages to get an accurate estimate.
# mtr -rw yourdomain.com -c 100
-cor--report-cycles– Set how many pings are sent to each hope to test its stability. (each cycle lasts one second)-ror--report– Run the test in the background, and when it's done, print out the results.-wor--report-wide– Make sure that the results list full hostnames instead of???
If you do not specify a number with the -c option, MTR will stop functioning after it has sent 10 packets.
To put MTR outcomes into a CSV file, do the following:
# mtr -rwC yourdomain.com -c 100 > mtr-results.csv
Output options:
-lor--raw-Cor--csv(separator is a semi-colon “;”)-jor--json-xor--xml
Conclusion��
Hopefully, you have learned how to use MTR command in Linux.
Also Read: How to Use Iperf to Test Network Performance
Thank You 🙂