MySQL Relational Databases on Ubuntu 12.04

*Introduction
MySQL is a relational database management system that is available for free online. You can say it like this: (RDBMS). The name comes from the combination of "My," which is the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter, and the acronym for Structured Query Language (SQL).
Web and server applications frequently use the well-liked database management system MySQL.
Installing, configuring, and managing MySQL will be covered in detail in this guide.
*Installing MySQL
#sudo apt-get install mysql-server
During installation, you'll be prompted to set a MySQL root password. Keep your password safe.
*MySQL Server secure installation
#sudo mysql_secure_installation
You can change MySQL's root password, remove anonymous user accounts, disable root database login outside localhost, and delete test databases. Yes is recommended. The MySQL Reference Manual has more details.
*Root Login
#mysql -u root -p
*After run this command you will face below interface
mysql>
*Make a New User in MySQL and Database
#create database microhostdb;
#create user 'microhost'@localhost identified by 'password';
#grant all on microhostdb.* to 'microhost';
*Creating the user and assigning database access privileges at the same time can speed up the process significantly:
#create database microhostdb;
#grant all on microhostdb.* to 'microhost' identified by 'password';
#exit
*Produce a Model of the Table.
#mysql -u microhost -p
#use microhostdb;
#create table customers (customer_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, first_name TEXT, last_name TEXT);
#exit
*Password-reset MySQL root user
You can reset your root MySQL password if you forget it.
*Stop the currently running MySQL server.
#sudo service mysql stop
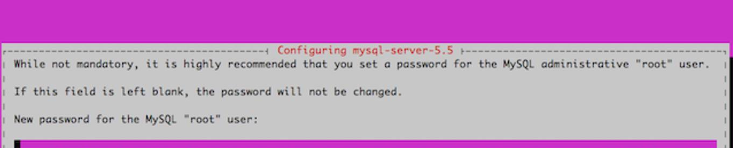
*Use dpkg to re-run the setup process that MySQL goes through the first time it is installed. You'll be asked to set a root password once more.
#sudo dpkg-reconfigure mysql-server-5.5
*You should now be able to log in once more by using the command mysql -u root -p.
*Tune MySQL
*From Ubuntu's software repositories, install MySQL Tuner.
#sudo apt-get install mysqltuner
*To operate it:
#mysqltuner
The output will include two sections of interest: general recommendations and variables to tweak.